Renal cells from spermatogonial germline stem cells protect against kidney injury
- PMID: 24136918
- PMCID: PMC3904562
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013040367
Renal cells from spermatogonial germline stem cells protect against kidney injury
Abstract
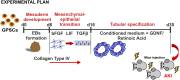
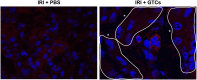
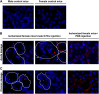
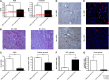
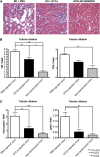
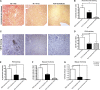
Spermatogonial stem cells reside in specific niches within seminiferous tubules and continuously generate differentiating daughter cells for production of spermatozoa. Although spermatogonial stem cells are unipotent, these cells are able to spontaneously convert to germline cell-derived pluripotent stem cells (GPSCs) in vitro. GPSCs have many properties of embryonic stem cells and are highly plastic, but their therapeutic potential in tissue regeneration has not been fully explored. Using a novel renal epithelial differentiation protocol, we obtained GPSC-derived tubular-like cells (GTCs) that were functional in vitro, as demonstrated through transepithelial electrical resistance analysis. In mice, GTCs injected after ischemic renal injury homed to the renal parenchyma, and GTC-treated mice showed reduced renal oxidative stress, tubular apoptosis, and cortical damage and upregulated tubular expression of the antioxidant enzyme hemeoxygenase-1. Six weeks after ischemic injury, kidneys of GTC-treated mice had less fibrosis and inflammatory infiltrate than kidneys of vehicle-treated mice. In conclusion, we show that GPSCs can be differentiated into functionally active renal tubular-like cells that therapeutically prevent chronic ischemic damage in vivo, introducing the potential utility of GPSCs in regenerative cell therapy.
Figures
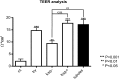


References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126: 663–676, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Lister R, Pelizzola M, Kida YS, Hawkins RD, Nery JR, Hon G, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, O’Malley R, Castanon R, Klugman S, Downes M, Yu R, Stewart R, Ren B, Thomson JA, Evans RM, Ecker JR: Hotspots of aberrant epigenomic reprogramming in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 471: 68–73, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

