Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain
- PMID: 24136970
- PMCID: PMC3880190
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1241224
Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain
Abstract
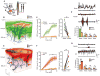
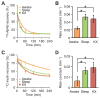
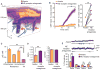
The conservation of sleep across all animal species suggests that sleep serves a vital function. We here report that sleep has a critical function in ensuring metabolic homeostasis. Using real-time assessments of tetramethylammonium diffusion and two-photon imaging in live mice, we show that natural sleep or anesthesia are associated with a 60% increase in the interstitial space, resulting in a striking increase in convective exchange of cerebrospinal fluid with interstitial fluid. In turn, convective fluxes of interstitial fluid increased the rate of β-amyloid clearance during sleep. Thus, the restorative function of sleep may be a consequence of the enhanced removal of potentially neurotoxic waste products that accumulate in the awake central nervous system.
Figures
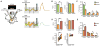
Comment in
-
Neuroscience. Sleep: the brain's housekeeper?Science. 2013 Oct 18;342(6156):301. doi: 10.1126/science.342.6156.301. Science. 2013. PMID: 24136944 No abstract available.
-
Neuroscience. Sleep it out.Science. 2013 Oct 18;342(6156):316-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1245798. Science. 2013. PMID: 24136954 No abstract available.
-
Sleep: Sleep: not such a waste.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Dec;14(12):816-7. doi: 10.1038/nrn3632. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24201183 No abstract available.
-
Alzheimer disease: Sleep alleviates AD-related neuropathological processes.Nat Rev Neurol. 2013 Dec;9(12):657. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.230. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24217519 No abstract available.
-
Wake up with a new brain!Mov Disord. 2014 Jan;29(1):33. doi: 10.1002/mds.25765. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Mov Disord. 2014. PMID: 24395717 No abstract available.
-
Sleep tight: a purpose for sleep.Neurosurgery. 2014 Feb;74(2):N17-8. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000442978.07078.e5. Neurosurgery. 2014. PMID: 24435147 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

