Scanning fluorescence correlation spectroscopy techniques to quantify the kinetics of DNA double strand break repair proteins after γ-irradiation and bleomycin treatment
- PMID: 24137007
- PMCID: PMC3874206
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt908
Scanning fluorescence correlation spectroscopy techniques to quantify the kinetics of DNA double strand break repair proteins after γ-irradiation and bleomycin treatment
Abstract
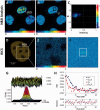
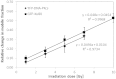
A common feature of DNA repair proteins is their mobilization in response to DNA damage. The ability to visualizing and quantifying the kinetics of proteins localizing/dissociating from DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) via immunofluorescence or live cell fluorescence microscopy have been powerful tools in allowing insight into the DNA damage response, but these tools have some limitations. For example, a number of well-established DSB repair factors, in particular those required for non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), do not form discrete foci in response to DSBs induced by ionizing radiation (IR) or radiomimetic drugs, including bleomycin, in living cells. In this report, we show that time-dependent kinetics of the NHEJ factors Ku80 and DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunits (DNA-PKcs) in response to IR and bleomycin can be quantified by Number and Brightness analysis and Raster-scan Image Correlation Spectroscopy. Fluorescent-tagged Ku80 and DNA-PKcs quickly mobilized in response to IR and bleomycin treatments consistent with prior reports using laser-generated DSBs. The response was linearly dependent on IR dose, and blocking NHEJ enhanced immobilization of both Ku80 and DNA-PKcs after DNA damage. These findings support the idea of using Number and Brightness and Raster-scan Image Correlation Spectroscopy as methods to monitor kinetics of DSB repair proteins in living cells under conditions mimicking radiation and chemotherapy treatments.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Ku can bind to nuclear DNA damage and sensitize mammalian cells to bleomycin sulfate.Mutagenesis. 2011 Nov;26(6):795-803. doi: 10.1093/mutage/ger049. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Mutagenesis. 2011. PMID: 21811007 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling damage complexity-dependent non-homologous end-joining repair pathway.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 10;9(2):e85816. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085816. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24520318 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Roles of Non-Homologous End Joining and Homologous Recombination in Repair of Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Double Strand Breaks in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells.Cells. 2024 Aug 30;13(17):1462. doi: 10.3390/cells13171462. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273031 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of DNA double strand break repair and chromosome aberration formation.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004;104(1-4):14-20. doi: 10.1159/000077461. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15162010 Review.
-
Roles for 53BP1 in the repair of radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Sep;93:102915. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102915. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33087281 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytoskeletal regulation of CD44 membrane organization and interactions with E-selectin.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35159-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.600767. Epub 2014 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25359776 Free PMC article.
-
New Methodologies to Study DNA Repair Processes in Space and Time Within Living Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 13;9:730998. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.730998. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34589495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering new balancer chromosomes in C. elegans via CRISPR/Cas9.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 21;6:33840. doi: 10.1038/srep33840. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27650892 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiated embryo chondrocyte plays a crucial role in DNA damage response via transcriptional regulation under hypoxic conditions.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 21;13(2):e0192136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192136. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29466367 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear structural protein NuMA is a negative regulator of 53BP1 in DNA double-strand break repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Apr 8;47(6):2703-2715. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz138. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30812030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khanna KK, Jackson SP. DNA double-strand breaks: signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat. Genet. 2001;27:247–254. - PubMed
-
- Hoeijmakers JH. Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature. 2001;411:366–374. - PubMed
-
- Burma S, Chen BP, Chen DJ. Role of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) in maintaining genomic integrity. DNA Repair. 2006;5:1042–1048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

