Olfactory consciousness and gamma oscillation couplings across the olfactory bulb, olfactory cortex, and orbitofrontal cortex
- PMID: 24137148
- PMCID: PMC3797617
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00743
Olfactory consciousness and gamma oscillation couplings across the olfactory bulb, olfactory cortex, and orbitofrontal cortex
Abstract
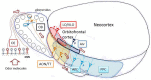
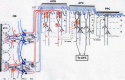
The orbitofrontal cortex receives multi-modality sensory inputs, including olfactory input, and is thought to be involved in conscious perception of the olfactory image of objects. Generation of olfactory consciousness may require neuronal circuit mechanisms for the "binding" of distributed neuronal activities, with each constituent neuron representing a specific component of an olfactory percept. The shortest neuronal pathway for odor signals to reach the orbitofrontal cortex is olfactory sensory neuron-olfactory bulb-olfactory cortex-orbitofrontal cortex, but other pathways exist, including transthalamic pathways. Here, we review studies on the structural organization and functional properties of the shortest pathway, and propose a model of neuronal circuit mechanisms underlying the temporal bindings of distributed neuronal activities in the olfactory cortex. We describe a hypothesis that suggests functional roles of gamma oscillations in the bindings. This hypothesis proposes that two types of projection neurons in the olfactory bulb, tufted cells and mitral cells, play distinct functional roles in bindings at neuronal circuits in the olfactory cortex: tufted cells provide specificity-projecting circuits which send odor information with early-onset fast gamma synchronization, while mitral cells give rise to dispersedly-projecting feed-forward binding circuits which transmit the response synchronization timing with later-onset slow gamma synchronization. This hypothesis also suggests a sequence of bindings in the olfactory cortex: a small-scale binding by the early-phase fast gamma synchrony of tufted cell inputs followed by a larger-scale binding due to the later-onset slow gamma synchrony of mitral cell inputs. We discuss that behavioral state, including wakefulness and sleep, regulates gamma oscillation couplings across the olfactory bulb, olfactory cortex, and orbitofrontal cortex.
Keywords: gamma synchronization; olfactory bulb; olfactory consciousness; olfactory cortex; orbitofrontal cortex; tufted and mitral cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sniff rhythm-paced fast and slow gamma-oscillations in the olfactory bulb: relation to tufted and mitral cells and behavioral states.J Neurophysiol. 2013 Oct;110(7):1593-9. doi: 10.1152/jn.00379.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 17. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23864376
-
Subpopulations of Projection Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb.Front Neural Circuits. 2020 Aug 28;14:561822. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2020.561822. eCollection 2020. Front Neural Circuits. 2020. PMID: 32982699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upstream γ-synchronization enhances odor processing in downstream neurons.Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 19;39(3):110693. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110693. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35443179
-
Task-Demand-Dependent Neural Representation of Odor Information in the Olfactory Bulb and Posterior Piriform Cortex.J Neurosci. 2019 Dec 11;39(50):10002-10018. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1234-19.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 31. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31672791 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Circuitry and Behavioral Decisions.Annu Rev Physiol. 2021 Feb 10;83:231-256. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-031820-092824. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Annu Rev Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33228453 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between Reaction Times and Post-COVID-19 Symptoms Assessed by a Web-Based Visual Detection Task.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;11(3):284. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11030284. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766859 Free PMC article.
-
Coherent olfactory bulb gamma oscillations arise from coupling independent columnar oscillators.J Neurophysiol. 2024 Mar 1;131(3):492-508. doi: 10.1152/jn.00361.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 24. J Neurophysiol. 2024. PMID: 38264784 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning of olfactory cortex ventral tenia tecta neurons to distinct task elements of goal-directed behavior.Elife. 2020 Aug 4;9:e57268. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57268. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32749216 Free PMC article.
-
Circuit formation and sensory perception in the mouse olfactory system.Front Neural Circuits. 2024 Feb 16;18:1342576. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2024.1342576. eCollection 2024. Front Neural Circuits. 2024. PMID: 38434487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible functional role of olfactory subsystems in monitoring inhalation and exhalation.Front Neuroanat. 2014 Sep 29;8:107. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2014.00107. eCollection 2014. Front Neuroanat. 2014. PMID: 25324732 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barkai E., Bergman R. E., Horwitz G., Hasselmo M. E. (1994). Modulation of associative memory function in a biophysical simulation of rat piriform cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 72, 659–677 - PubMed
-
- Barkai E., Hasselmo M. E. (1994). Modulation of the input/output function of rat piriform cortex pyramidal cells. J. Neurophysiol. 72, 644–658 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

