Characterization of β-cell function and insulin resistance in overweight Chinese adolescents with normal glucose tolerance
- PMID: 24137224
- PMCID: PMC3786842
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2013.1164
Characterization of β-cell function and insulin resistance in overweight Chinese adolescents with normal glucose tolerance
Abstract
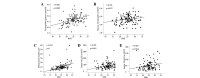
This study aimed to investigate the characteristics of insulin resistance and β-cell secretion in healthy adolescents. A total of 124 adolescents with normal glucose tolerance (NGT) were divided according to BMI into normal weight (n=31; control), overweight (n=52) and obese (n=41) groups. Oral glucose tolerance tests were performed, and blood glucose (G0, G30 and G120) and insulin (I0, I30 and I120) levels at 0, 30 and 120 min, respectively, were measured. The homeostasis model assessment estimate of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and early insulin release index (IRI) were calculated to evaluate insulin sensitivity and early β-cell secretion. The G0, G120 levels and the natural logarithm (Ln) of I30 and ΔI30/ΔG30 were similar in the overweight and obese groups, but significantly higher compared with those of the normal weight group (P<0.05). LnI0 and LnHOMA-IR progressively increased (P<0.01) in correlation with the degree of obesity among the three groups. LnΔI30/ΔG30 and LnHOMA-IR were significantly positively correlated with the indices of obesity (P<0.001 and P<0.05, respectively). LnHOMA-IR was also positively correlated with the insulin levels at 30 and 120 min (r=0.454 and 0.314, respectively; P<0.001). In healthy adolescents, insulin resistance progressively increased with increased body mass index (BMI), but the compensatory increase in early insulin secretion was limited.
Keywords: adolescent; insulin resistance; islet cell; overweight; secretion.
Figures



References
-
- Ji CY, Sun JL, Chen TJ. Dynamic analysis on the prevalence of obesity and overweight school-age children and adolescents in recent 15 years in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2004;25:103–108. (In Chinese). - PubMed
-
- Chen CM. Overview of obesity in Mainland China. Obes Rev. 2008;9(Suppl 1):14–21. - PubMed
-
- Johnson WD, Kroon JJ, Greenway FL, Bouchard C, Ryan D, Katzmarzyk PT. Prevalence of risk factors for metabolic syndrome in adolescents: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 2001–2006. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2009;163:371–377. - PubMed
-
- Mitrakou A, Kelley D, Mokan M, et al. Role of reduced suppression of glucose production and diminished early insulin release in impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:22–29. - PubMed
-
- Weiss R, Gillis D. Patho-physiology and dynamics of altered glucose metabolism in obese children and adolescents. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2008;3(Suppl 1):15–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
