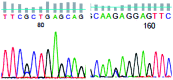
Keap1 mutations in lung cancer patients
- PMID: 24137397
- PMCID: PMC3789102
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2013.1427
Keap1 mutations in lung cancer patients
Abstract
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) inhibits nuclear factor erythroid 2-related 2 (NEF2L2; also named NRF2)-induced cytoprotection and has been hypothesized to represent a candidate tumor suppressor. We have previously reported the somatic mutations of the NRF2 gene (NFE2L2), however, the correlation between the Keap1 mutation and the clinicopathological features of lung cancer has not been well investigated. Therefore, in the present study, the Keap1 mutational status in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients was investigated by reverse transcription PCR and direct sequencing. The study included 76 surgically-removed lung cancer cases from patients of the Nagoya City University Hospital in which the EGFR and NFE2L2 mutation status was already established. Keap1 mutations were identified in 2 (2.6%) adenocarcinoma patients with a history of heavy smoking. These mutations were identified to exist exclusively. The Keap1 mutation was only detected in patients with advanced adenocarcinoma (4.3%) and the completely exclusive status of this mutation and others, including EGFR, Kas, erbB2 and NRF2L2, is likely to improve the selection of personalized therapy for lung cancer.
Keywords: Keap1; NRF2; adenocarcinoma; lung cancer; mutations.
Figures
References
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. New Eng J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki H, Endo H, Konishi A, et al. EGFR mutation status in Japanese lung cancer patients: genotyping analysis using LightCycler. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2924–2929. - PubMed
-
- Soda H, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous