Effects of gamma irradiation on cell cycle, apoptosis and telomerase activity in p53 wild-type and deficient HCT116 colon cancer cell lines
- PMID: 24137415
- PMCID: PMC3789084
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2013.1441
Effects of gamma irradiation on cell cycle, apoptosis and telomerase activity in p53 wild-type and deficient HCT116 colon cancer cell lines
Abstract
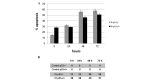
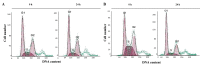
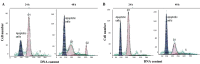
Radiotherapy serves as adjunctive treatment to chemotherapy and surgical resection of colorectal cancer. However, the cellular response to irradiation varies depending on the expression of tumor suppressor p53, which plays a significant role in the regulation of cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and telomerase activity in various cancers. The present study aimed to investigate cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and telomerase activity with respect to p53 expression in p53 wild-type (+/+) and deficient (-/-) HCT116 colon cancer cell lines following 5 Gy γ-irradiation. Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis were evaluated using flow cytometry. The telomerase activity was measured using a TRAP (telomerase repeat amplification protocol) assay. Following treatment with irradiation, G1/S cell cycle arrest occurred in the p53+/+ cells, whereas the p53-/- cells accumulated in the G2 phase. No differences were observed in the apoptotic ratios between the two cell lines following irradiation. Decreased telomerase activity was observed in the p53+/+ cells, whereas telomerase activity was increased in the p53-/- cells. The results showed that while telomerase activity and G1 cell cycle arrest were regulated depending on the p53 status, G2 arrest and the apoptotic response were promoted via a p53-independent pathway.
Keywords: apoptosis; cell proliferation; irradiation; p53; telomerase activity.
Figures
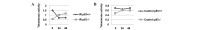
Similar articles
-
Role of p53 in G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in response to gamma-irradiation in ovarian carcinoma cell lines.Int J Oncol. 2003 Jan;22(1):51-7. Int J Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12469184
-
Adenovirus-mediated p53 gene transduction inhibits telomerase activity independent of its effects on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 1999 Aug;5(8):2140-7. Clin Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10473098
-
Selenomethionine induces p53 mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 May;5(5):529-35. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.5.2654. Epub 2006 May 5. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16627976
-
p53-Dependent accelerated senescence induced by ionizing radiation in breast tumour cells.Int J Radiat Biol. 2005 Jun;81(6):445-58. doi: 10.1080/09553000500168549. Int J Radiat Biol. 2005. PMID: 16308915
-
The small molecule AU14022 promotes colorectal cancer cell death via p53-mediated G2/M-phase arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jun;233(6):4666-4676. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26234. Epub 2018 Jan 15. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29030986
Cited by
-
Omacetaxine mepesuccinate induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, promotes cell differentiation, and reduces telomerase activity in diffuse large B‑cell lymphoma cells.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Apr;13(4):3092-100. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.4899. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26935769 Free PMC article.
-
The Growing Complexity of Cancer Cell Response to DNA-Damaging Agents: Caspase 3 Mediates Cell Death or Survival?Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 11;17(5):708. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050708. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27187358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In HPV-Positive HNSCC Cells, Functional Restoration of the p53/p21 Pathway by Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib Does Not Affect Radio- or Chemosensitivity.Transl Oncol. 2019 Mar;12(3):417-425. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.11.013. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30554133 Free PMC article.
-
The p53 Protein Family in the Response of Tumor Cells to Ionizing Radiation: Problem Development.Acta Naturae. 2021 Jul-Sep;13(3):65-76. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.11247. Acta Naturae. 2021. PMID: 34707898 Free PMC article.
-
p38α MAPK-mediated induction and interaction of FOXO3a and p53 contribute to the inhibited-growth and induced-apoptosis of human lung adenocarcinoma cells by berberine.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Apr 26;33(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-36. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24766860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fearon ER, Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990;61:759–767. - PubMed
-
- Caspari T. How to activate p53. Curr Biol. 2000;10:R315–R317. - PubMed
-
- Brooks CL, Gu W. Ubiquitination, phosphorylation and acetylation: the molecular basis for p53 regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:164–171. - PubMed
-
- Liang SH, Clarke MF. Regulation of p53 localization. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:2779–2783. - PubMed
-
- Adimoolam S, Ford JM. p53 regulation of DNA damage recognition during nucleotide excision repair. DNA Repair (Amst) 2003;2:947–954. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
