Novel vasocontractile role of the P2Y₁₄ receptor: characterization of its signalling in porcine isolated pancreatic arteries
- PMID: 24138077
- PMCID: PMC3969082
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12473
Novel vasocontractile role of the P2Y₁₄ receptor: characterization of its signalling in porcine isolated pancreatic arteries
Abstract
Background and purpose: The P2Y₁₄ receptor is the newest member of the P2Y receptor family; it is G(i/o) protein-coupled and is activated by UDP and selectively by UDP-glucose and MRS2690 (2-thiouridine-5'-diphosphoglucose) (7-10-fold more potent than UDP-glucose). This study investigated whether P2Y₁₄ receptors were functionally expressed in porcine isolated pancreatic arteries.
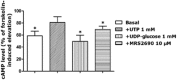
Experimental approach: Pancreatic arteries were prepared for isometric tension recording and UDP-glucose, UDP and MRS2690 were applied cumulatively after preconstriction with U46619, a TxA₂ mimetic. Levels of phosphorylated myosin light chain 2 (MLC2) were assessed with Western blotting. cAMP concentrations were assessed using a competitive enzyme immunoassay kit.
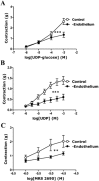
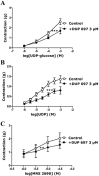
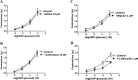
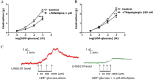
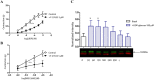
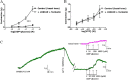
Key results: Concentration-dependent contractions with a rank order of potency of MRS2690 (10-fold) > UDP-glucose ≥ UDP were recorded. These contractions were reduced by PPTN {4-[4-(piperidin-4-yl)phenyl]-7-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2-naphthoic acid}, a selective antagonist of P2Y₁₄ receptors, which did not affect responses to UTP. Contraction to UDP-glucose was not affected by MRS2578, a P2Y₆ receptor selective antagonist. Raising cAMP levels and forskolin, in the presence of U46619, enhanced contractions to UDP-glucose. In addition, UDP-glucose and MRS2690 inhibited forskolin-stimulated cAMP levels. Removal of the endothelium and inhibition of endothelium-derived contractile agents (TxA₂, PGF(2α) and endothelin-1) inhibited contractions to UDP glucose. Y-27632, nifedipine and thapsigargin also reduced contractions to the agonists. UDP-glucose and MRS2690 increased MLC2 phosphorylation, which was blocked by PPTN.
Conclusions and implications: P2Y₁₄ receptors play a novel vasocontractile role in porcine pancreatic arteries, mediating contraction via cAMP-dependent mechanisms, elevation of intracellular Ca²⁺ levels, activation of RhoA/ROCK signalling and MLC2, along with release of TxA₂, PGF(2α) and endothelin-1.
Keywords: MRS2690; P2Y14 receptor; UDP; UDP-glucose; endothelium; vasoconstriction.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Abbas Z, Latif L, Ralevic V. 2011. Effects of P2Y14 receptor agonists, UDP-glucose and MRS2690, on porcine coronary artery contractility. Available at: http://www.pA2online.org/abstracts/Vol9Issue3abst051p.pdf (accessed 4/9/2012)
-
- Alsaqati M, Latif LL, Chan SLF, Ralevic R. 2010. Identification of the novel P2Y14 receptor in porcine isolated pancreatic arteries. Available at: http://www.pa2online.org/abstracts/vol8issue1abst028p.pdf (accessed 4/9/2012)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

