Fixing frataxin: 'ironing out' the metabolic defect in Friedreich's ataxia
- PMID: 24138602
- PMCID: PMC3976629
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12470
Fixing frataxin: 'ironing out' the metabolic defect in Friedreich's ataxia
Abstract
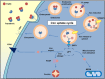
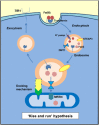
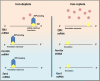
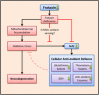
The metabolically active and redox-active mitochondrion appears to play a major role in the cellular metabolism of the transition metal, iron. Frataxin, a mitochondrial matrix protein, has been identified as playing a key role in the iron metabolism of this organelle due to its iron-binding properties and is known to be essential for iron-sulphur cluster formation. However, the precise function of frataxin remains elusive. The decrease in frataxin expression, as seen in the inherited disorder Friedreich's ataxia, markedly alters cellular and mitochondrial iron metabolism in both the mitochondrion and the cell. The resulting dysregulation of iron trafficking damages affects tissues leading to neuro- and cardiodegeneration. This disease underscores the importance of iron homeostasis in the redox-active environment of the mitochondrion and the molecular players involved. Unravelling the mechanisms of altered iron metabolism in Friedreich's ataxia will help elucidate a biochemical function for frataxin. Consequently, this will enable the development of more effective and rationally designed treatments. This review will focus on the emerging function of frataxin in relation to the observed alterations in mitochondrial iron metabolism in Friedreich's ataxia. Tissue-specific alterations due to frataxin loss will also be discussed, as well as current and emerging therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Friedreich's ataxia; autophagy; cardio- and neurodegeneration; frataxin; mitochondrial iron accumulation; oxidative stress.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Adinolfi S, Trifuoggi M, Politou AS, Martin S, Pastore A. A structural approach to understanding the iron-binding properties of phylogenetically different frataxins. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:1865–1877. - PubMed
-
- Adinolfi S, Iannuzzi C, Prischi F, Pastore C, Iametti S, Martin SR, et al. Bacterial frataxin cyay is the gatekeeper of iron-sulfur cluster formation catalyzed by iscs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16:390–396. - PubMed
-
- Aisen P, Brown EB. The iron-binding function of transferrin in iron metabolism. Semin Hematol. 1977;14:31–53. - PubMed
-
- Allikmets R, Raskind WH, Hutchinson A, Schueck ND, Dean M, Koeller DM. Mutation of a putative mitochondrial iron transporter gene (abc7) in x-linked sideroblastic anemia and ataxia (xlsa/a) Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:743–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

