Antidepressant-like effects of the aqueous macerate of the bulb of Gladiolus dalenii Van Geel (Iridaceae) in a rat model of epilepsy-associated depression
- PMID: 24138845
- PMCID: PMC3854025
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-272
Antidepressant-like effects of the aqueous macerate of the bulb of Gladiolus dalenii Van Geel (Iridaceae) in a rat model of epilepsy-associated depression
Abstract
Background: In Cameroonian traditional medicine various extracts of Gladiolus dalenii Van Geel (Iridaceae) have been used as a cure for various ailments that include headaches, digestive problems, muscle and joint aches, and some central nervous system disorders such as epilepsy, schizophrenia and mood disorders. Owning to this background, the aim of the study was to investigate whether an aqueous macerate of the bulb of Gladiolus dalenii has any antidepressant activity focusing specifically on depression-like behaviours associated with epilepsy.
Method: We used the combined administration of atropine and pilocarpine to rats as our animal model of epilepsy. The forced swim test and spontaneous locomotor activity in the open field test were the two tools used to assess the presence of depression-like behaviour in epileptic and control animals. The following depression-related parameters were determined: plasma ACTH, plasma corticosterone, adrenal gland weight and hippocampal levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). The effects of Gladiolus dalenii were compared to that of fluoxetine.
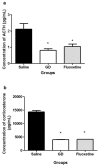
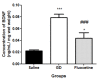
Results: Our results showed that we had a valid animal model of epilepsy-induced depression as all 3 measures of construct, predictive and face validity were satisfied. The data indicated that Gladiolus dalenii significantly reduced the immobility times in the forced swim test and the locomotor activity as assessed in the open field. A similar pattern was observed when the HPA axis parameters were analysed. Gladiolus dalenii significantly reduced the levels of ACTH, corticosterone, but not the adrenal gland weight. Gladiolus dalenii significantly increased the level of BDNF in the hippocampus. In all parameters measured the effects of Gladiolus dalenii were significantly greater than those of fluoxetine.
Conclusion: The results show that Gladiolus dalenii has antidepressant-like properties similar to those of fluoxetine in epilepsy-associated depressive states. The antidepressant activity of Gladiolus dalenii is likely to be mediated by restoring the activity of the HPA axis and increasing the levels of BDNF in the hippocampus.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antidepressant properties of aqueous macerate from Gladiolus dalenii corms.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2013 Nov 2;11(1):53-61. eCollection 2014. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2013. PMID: 24653553 Free PMC article.
-
Gladiolus dalenii lyophilisate reverses scopolamine-induced amnesia and reduces oxidative stress in rat brain.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jul;91:350-357. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.061. Epub 2017 May 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28463798
-
Piper sarmentosum Roxb. produces antidepressant-like effects in rodents, associated with activation of the CREB-BDNF-ERK signaling pathway and reversal of HPA axis hyperactivity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Mar 6;199:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.037. Epub 2017 Jan 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28126450
-
[Strategy to develop a new drug for treatment-resistant depression--role of electroconvulsive stimuli and BDNF].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007 Apr;127(4):735-42. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.127.735. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17409705 Review. Japanese.
-
Elucidating the Possible Role of FoxO in Depression.Neurochem Res. 2021 Nov;46(11):2761-2775. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03364-4. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 34075521 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined corticosterone treatment and chronic restraint stress lead to depression associated with early cognitive deficits in mice.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Apr;33(2):421-431. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0148-4. Epub 2017 Dec 3. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 29199383
-
Recent Studies on Anti-Depressant Bioactive Substances in Selected Species from the Genera Hemerocallis and Gladiolus: A Systematic Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019 Nov 25;12(4):172. doi: 10.3390/ph12040172. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31775329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Culture Technology and Advanced Biotechnology Tools Toward Improvement in Gladiolus (Gladiolus species): Present Scenario and Future Prospects.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;66(8):1806-1835. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00818-8. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37528332 Review.
-
Depression in Sub-Saharan Africa.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 Mar 17;12:309-322. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.03.005. eCollection 2022 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35746974 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective and Antiamnesic Effects of Mitragyna inermis Willd (Rubiaceae) on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice.Behav Neurol. 2017;2017:5952897. doi: 10.1155/2017/5952897. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Behav Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28386162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kessler RC. Prevalence, severity, and unmet need for treatment of mental disorders in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. J Am Med Assoc. 2004;291:2581–2590. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg JM. Medicines for treating depression: a review of the research for adults. AHRQ Comp Eff Rev. 2012. http://www.ahrq.gov. - PubMed
-
- Frazer A. Pharmacology of antidepressants. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1997;17(1):2–18. - PubMed
-
- Mahomoodally MF. In: Medicinal Plants: Biodiversity and Drugs. Rai MK, Cordell G, Jose LM, editor. New York, USA: Science Publishers CRC Press: Taylor and Francis; 2012. Recent advances to evaluate anti-diabetic medicinal plants; pp. 526–569.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

