Cardiac positron emission tomography enhances prognostic assessments of patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis
- PMID: 24140661
- PMCID: PMC3955730
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.09.022
Cardiac positron emission tomography enhances prognostic assessments of patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis
Abstract
Objectives: This study sought to relate imaging findings on positron emission tomography (PET) to adverse cardiac events in patients referred for evaluation of known or suspected cardiac sarcoidosis.
Background: Although cardiac PET is commonly used to evaluate patients with suspected cardiac sarcoidosis, the relationship between PET findings and clinical outcomes has not been reported.
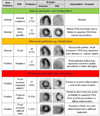
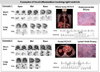
Methods: We studied 118 consecutive patients with no history of coronary artery disease, who were referred for PET, using [(18)F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) to assess for inflammation and rubidium-82 to evaluate for perfusion defects (PD), following a high-fat/low-carbohydrate diet to suppress normal myocardial glucose uptake. Blind readings of PET data categorized cardiac findings as normal, positive PD or FDG, positive PD and FDG. Images were also used to identify whether findings of extra-cardiac sarcoidosis were present. Adverse events (AE)-death or sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT)-were ascertained by electronic medical records, defibrillator interrogation, patient questionnaires, and telephone interviews.
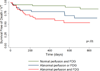
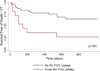
Results: Among the 118 patients (age 52 ± 11 years; 57% males; mean ejection fraction: 47 ± 16%), 47 (40%) had normal and 71 (60%) had abnormal cardiac PET findings. Over a median follow-up of 1.5 years, there were 31 (26%) adverse events (27 VT and 8 deaths). Cardiac PET findings were predictive of AE, and the presence of both a PD and abnormal FDG (29% of patients) was associated with hazard ratio of 3.9 (p < 0.01) and remained significant after adjusting for left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and clinical criteria. Extra-cardiac FDG uptake (26% of patients) was not associated with AE.
Conclusions: The presence of focal PD and FDG uptake on cardiac PET identifies patients at higher risk of death or VT. These findings offer prognostic value beyond Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare clinical criteria, the presence of extra-cardiac sarcoidosis and LVEF.
Keywords: CMR; CT; EMBx; FDG; ICD; JMHW; Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare; LVEF; PET; RV; VT; cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; computed tomography; endomyocardial biopsy; fluorodeoxyglucose; implantable cardiac defibrillator; left ventricular ejection fraction; positron emission tomography; prognosis; right ventricular; sarcoidosis; ventricular tachycardia.
Copyright © 2014 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reply: Cardiac positron emission tomography as a prognostic indicator of cardiac sarcoidosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Jun 17;63(23):2590. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.604. Epub 2014 Apr 9. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24727253 No abstract available.
-
Cardiac positron emission tomography as a prognostic indicator of cardiac sarcoidosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Jun 17;63(23):2589-2590. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.01.076. Epub 2014 Apr 9. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24727255 No abstract available.
-
18F-FDG imaging in patients with "suspected," but not "proven," sarcoidosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Aug 12;64(6):630. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.055. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25104536 No abstract available.
-
Reply: (18)F-FDG imaging in patients with "suspected," but not "proven," sarcoidosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Aug 12;64(6):631. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.05.023. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25104538 No abstract available.
References
-
- Silverman KJ, Hutchins GM, Bulkley BH. Cardiac sarcoid: a clinicopathologic study of 84 unselected patients with systemic sarcoidosis. Circulation. 1978;58:1204–1211. - PubMed
-
- Cooper LT, Baughman KL, Feldman AM, et al. The role of endomyocardial biopsy in the management of cardiovascular disease. European Heart Journal. 2007;28:3076–3093. - PubMed
-
- Youssef G, Leung E, Mylonas I, et al. The Use of 18F-FDG PET in the Diagnosis of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis Including the Ontario Experience. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Yamagishi H, Shirai N, Takagi M, et al. Identification of cardiac sarcoidosis with (13)NNH(3)/(18)F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 2003;44:1030–1036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

