Spatial delayed nonmatching-to-sample performances in long-living Ames dwarf mice
- PMID: 24140989
- PMCID: PMC6431547
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.10.001
Spatial delayed nonmatching-to-sample performances in long-living Ames dwarf mice
Abstract
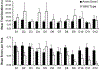
Ames dwarf mice have an extended lifespan by comparison with normal mice. Behavioral testing has revealed that sometimes Ames dwarf mice also evince superior performances relative to normal mice, but in other cases they do not. In this experiment, Ames dwarf and normal mice were compared on a T-maze test and on a delayed nonmatching-to-sample variant of a T-maze test. On the simple T-maze, Ames dwarf and normal mice committed comparable numbers of errors. On the nonmatching-to-sample task, normal mice mastered the discrimination by the end of the experiment while Ames dwarf mice did not. The apparatus, distances traveled and session duration were equivalent between the two tasks. The poorer performances of Ames dwarf mice on the nonmatching-to-sample task suggests that Ames dwarf mice may not be as capable of learning relatively cognitively complex tasks as normal mice.
Keywords: Aging; Ames dwarf mouse; Learning; Longevity; Reinforcement.
© 2013.
Figures

References
-
- Bartke A Histology of the anterior hypophysis, thyroid and gonads of two types of dwarf mice. Anat Rec 1964;149:225–35. - PubMed
-
- Sornson MW, Wu W, Dasen JS, Flynn SE, Norman DJ, O’Connell SM, et al. Pituitary lineage determination by the prophet of pit-1 homeodomain factor defective in Ames dwarfism. Nature 1996;384:327–33. - PubMed
-
- Bartke A, Wright JC, Mattison J, Ingram DK, Miller RA, Roth GS. Extending the lifespan of long-lived mice. Nature 2001;414:412. - PubMed
-
- Brown-Borg H Hormonal regulation of aging and life span. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2003;14:151–3. - PubMed
-
- Amador-Noguez D, Zimmerman J, Venable S, Darlington G. Gender-specific alterations in gene expression and loss of liver sexual dimorphism in the long-lived Ames dwarf mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005;332:1086–100. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

