Evidence that collaboration between HIF-1α and Notch-1 promotes neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke
- PMID: 24141018
- PMCID: PMC3877697
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.10.009
Evidence that collaboration between HIF-1α and Notch-1 promotes neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke
Abstract
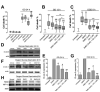
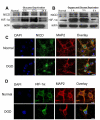
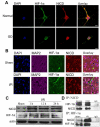
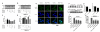
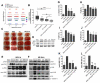
Recent findings suggest that Notch-1 signaling contributes to neuronal death in ischemic stroke, but the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), a global regulator of cellular responses to hypoxia, can interact with Notch and modulate its signaling during hypoxic stress. Here we show that Notch signaling interacts with the HIF-1α pathway in the process of ischemic neuronal death. We found that a chemical inhibitor of the Notch-activating enzyme, γ-secretase, and a HIF-1α inhibitor, protect cultured cortical neurons against ischemic stress, and combined inhibition of Notch-1 and HIF-1α further decreased neuronal death. HIF-1α and Notch intracellular domain (NICD) are co-expressed in the neuronal nucleus, and co-immunoprecipitated in cultured neurons and in brain tissue from mice subjected to focal ischemic stroke. Overexpression of NICD and HIF-1α in cultured human neural cells enhanced cell death under ischemia-like conditions, and a HIF-1α inhibitor rescued the cells. RNA interference-mediated depletion of endogenous NICD and HIF-1α also decreased cell death under ischemia-like conditions. Finally, mice treated with inhibitors of γ-secretase and HIF-1α exhibited improved outcome after focal ischemic stroke, with combined treatment being superior to individual treatments. Additional findings suggest that the NICD and HIF-1α collaborate to engage pro-inflammatory and apoptotic signaling pathways in stroke.
Keywords: Apoptosis; HIF-1α; Ischemic stroke; Neuronal cell death; Notch.
© 2013.
Figures
References
-
- Arumugam TV, Chan SL, Jo DG, Yilmaz G, Tang SC, Cheng A, Gleichmann M, Okun E, Dixit VD, Chigurupati S, Mughal MR, Ouyang X, Miele L, Magnus T, Poosala S, Granger DN, Mattson MP. Gamma secretase-mediated Notch signaling worsens brain damage and functional outcome in ischemic stroke. Nat Med. 2006;12:621–623. - PubMed
-
- Arumugam TV, Cheng YL, Choi Y, Choi YH, Yang S, Yun YK, Park JS, Yang DK, Thundyil J, Gelderblom M, Karamyan VT, Tang SC, Chan SL, Magnus T, Sobey CG, Jo DG. Evidence that gamma-secretase-mediated Notch signaling induces neuronal cell death via the nuclear factor-kappaB-Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death pathway in ischemic stroke. Mol Pharmacol. 2011;80:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Arumugam TV, Salter JW, Chidlow JH, Ballantyne CM, Kevil CG, Granger DN. Contributions of LFA-1 and Mac-1 to brain injury and microvascular dysfunction induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;287:H2555–2560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

