COUP-TFII inhibits NFkappaB activation in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells
- PMID: 24141032
- PMCID: PMC5089806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.10.010
COUP-TFII inhibits NFkappaB activation in endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells
Abstract
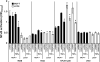
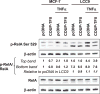
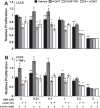
Reduced COUP-TFII expression contributes to endocrine resistance in breast cancer cells. Endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells have higher NFkappa B (NFκB) activity and target gene expression. The goal of this study was to determine if COUP-TFII modulates NFκB activity. Endocrine-resistant LCC9 cells with low endogenous COUP-TFII displayed ∼5-fold higher basal NFκB activity than parental endocrine-sensitive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Transient transfection of LCC9 cells with COUP-TFII inhibited NFκB activation and reduced NFκB target gene expression. COUP-TFII and NFκB were inversely correlated in breast cancer patient samples. Endogenous COUP-TFII coimmunoprecipitated with NFκB subunits RelB and NFκB1 in MCF-7 cells. COUP-TFII inhibited NFκB-DNA binding in vitro and impaired coactivator induced NFκB transactivation. LCC9 cells were growth-inhibited by an NFκB inhibitor and 4-hydroxytamoxifen compared to MCF-7 cells. Together these data indicate a novel role for COUP-TFII in suppression of NFκB activity and explain, in part, why decreased COUP-TFII expression results in an endocrine-resistant phenotype.
Keywords: 4-OHT; 4-hydroxytamoxifen; A20/TNFAIP3; Antiestrogens; COUP-TFII; Drug resistance; ERα; ICAM1; IL6; NFκB/NFkappa B; Nuclear receptors; RE; SERD; SERM; TAM; TNFα; TNFα-induced protein 3; Tamoxifen; Transcription factors; chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II; estrogen receptor; intercellular adhesion molecule 1; interleukin 6 (IL6); nuclear factor κB; qPCR; quantitative real-time PCR; response element; selective estrogen receptor downregulator; selective estrogen receptor modulator; tamoxifen; tumor necrosis factor.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
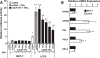
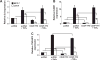



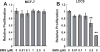
References
-
- Bren GD, Solan NJ, Miyoshi H, Pennington KN, Pobst LJ, Paya CV. Transcription of the RelB gene is regulated by NF-kappaB. Oncogene. 2001;20:7722–7733. - PubMed
-
- Brunner N, Boysen B, Jirus S, Skaar TC, Holst-Hansen C, Lippman J, Frandsen T, Spang-Thomsen M, Fuqua SA, Clarke R. MCF7/LCC9: an antiestrogen-resistant MCF-7 variant in which acquired resistance to the steroidal antiestrogen ICI 182,780 confers an early cross-resistance to the nonsteroidal antiestrogen tamoxifen. Cancer Res. 1997;57:3486–3493. - PubMed
-
- Burke JR, Pattoli MA, Gregor KR, Brassil PJ, MacMaster JF, McIntyre KW, Yang X, Iotzova VS, Clarke W, Strnad J, Qiu Y, Zusi FC. BMS-345541 is a highly selective inhibitor of I kappa B kinase that binds at an allosteric site of the enzyme and blocks NF-kappa B-dependent transcription in mice. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1450–1456. - PubMed
-
- Chew J, Biswas S, Shreeram S, Humaidi M, Wong ET, Dhillion MK, Teo H, Hazra A, Fang CC, Lopez-Collazo E, Bulavin DV, Tergaonkar V. WIP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:659–666. - PubMed
-
- Cogswell PC, Guttridge DC, Funkhouser WK, Baldwin AS., Jr Selective activation of NF-kappa B subunits in human breast cancer: potential roles for NF-kappa B2/p52 and for Bcl-3. Oncogene. 2000;19:1123–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

