Thymosin ß4 expression in colorectal polyps and adenomas
- PMID: 24141838
- PMCID: PMC3782725
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2013(09)08
Thymosin ß4 expression in colorectal polyps and adenomas
Abstract
Objective: Thymosin beta 4 (Tβ4) is a ubiquitous peptide that plays pivotal roles in the cytoskeletal system and in cell differentiation. Recently, a role for Tβ4 has been proposed in experimental and human carcinogenesis, including gastrointestinal cancer. This study was aimed at evaluating the relationship between Tβ4 immunoreactivity and the initial steps of carcinogenesis.
Methods: In total, 60 intestinal biopsies, including 10 hyperplastic polyps, 10 sessile serrated adenomas/polyps, 15 colorectal adenomas with low-grade dysplasia, 15 adenomas with high-grade dysplasia, 15 adenocarcinomas and 10 samples of normal colon mucosa, were analyzed for Tβ4 expression by immunohistochemistry.
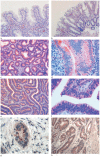
Results: Weak cytoplasmic reactivity for Tβ4 was detected in the normal colon mucosa. No reactivity for Tβ4 was found in hyperplastic and sessile serrated polyps/adenomas. Tβ4 expression was observed in 10/15 colorectal adenocarcinomas. In adenomas with low-grade dysplasia, Tβ4 immunoreactivity was mainly detected in dysplastic glands but was absent in hyperplastic glands. Tβ4 immunoreactivity was characterized by spot-like perinuclear staining. In high-grade dysplastic polyps, immunostaining for Tβ4 appeared diffuse throughout the entire cytoplasm of dysplastic cells. Spot-like perinuclear reactivity was detected in adenocarcinoma tumor cells.
Conclusions: Our study shows for the first time that Tβ4 is expressed during different steps of colon carcinogenesis. The shift of Tβ4 immunolocalization from low-grade to high-grade dysplastic glands suggests a role for Tβ4 in colorectal carcinogenesis. However, the real meaning of Tβ4 reactivity in dysplastic intestinal epithelium remains unknown.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histologic and molecular analyses of colonic perineurial-like proliferations in serrated polyps: perineurial-like stromal proliferations are seen in sessile serrated adenomas.Am J Surg Pathol. 2011 Sep;35(9):1373-80. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318224d9df. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21836484
-
MCM2 expression in serrated polyps demonstrates aberrant cellular proliferation.Hum Pathol. 2017 May;63:177-183. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.02.020. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28302537
-
Ki-67, p53, and Bcl-2 expression of serrated adenomas of the colon.Am J Surg Pathol. 1997 Apr;21(4):417-23. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199704000-00007. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997. PMID: 9130988
-
Three Pathways of Colonic Carcinogenesis in Rats.Anticancer Res. 2017 Jan;37(1):15-20. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11284. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28011469 Review.
-
Colorectal Cancer Screening for the Serrated Pathway.Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020 Jul;30(3):457-478. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2020.02.007. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020. PMID: 32439082 Review.
Cited by
-
MALDI-imaging reveals thymosin beta-4 as an independent prognostic marker for colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 22;6(41):43869-80. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6103. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26556858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mannherz HG, Hannappel E. The β-thymosins: intracellular and extracellular activities of a versatile actin binding protein family. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009;66(10):839–51. - PubMed
-
- Koutrafouri V, Leondiadis L, Avgoustakis K, Livaniou E, Czarneki J, Ithakissios DS, et al. Effect of thymosin peptides on the chick chorioallantoic membrane angiogenesis model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1568(1):60–6. - PubMed
-
- Malinda KM, Sidhu GS, Mani H, Banaudha K, Maheshwari K, Goldstein AL, et al. Thymosin beta 4 accelerates wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 1999;113(3):364–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

