ExsA and LcrF recognize similar consensus binding sites, but differences in their oligomeric state influence interactions with promoter DNA
- PMID: 24142246
- PMCID: PMC3889609
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00990-13
ExsA and LcrF recognize similar consensus binding sites, but differences in their oligomeric state influence interactions with promoter DNA
Abstract
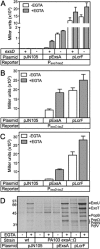
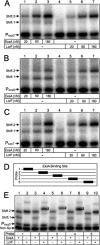
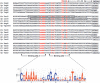
ExsA activates type III secretion system (T3SS) gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and is a member of the AraC family of transcriptional regulators. AraC proteins contain two helix-turn-helix (HTH) DNA binding motifs. One helix from each HTH motif inserts into the major groove of the DNA to make base-specific contacts with the promoter region. The amino acids that comprise the HTH motifs of ExsA are nearly identical to those in LcrF/VirF, the activators of T3SS gene expression in the pathogenic yersiniae. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that ExsA/LcrF/VirF recognize a common nucleotide sequence. We report that Yersinia pestis LcrF binds to and activates transcription of ExsA-dependent promoters in P. aeruginosa and that plasmid-expressed ExsA complements a Y. pestis lcrF mutant for T3SS gene expression. Mutations that disrupt the ExsA consensus binding sites in both P. aeruginosa and Y. pestis T3SS promoters prevent activation by ExsA and LcrF. Our combined data demonstrate that ExsA and LcrF recognize a common nucleotide sequence. Nevertheless, the DNA binding properties of ExsA and LcrF are distinct. Whereas two ExsA monomers are sequentially recruited to the promoter region, LcrF binds to promoter DNA as a preformed dimer and has a higher capacity to bend DNA. An LcrF mutant defective for dimerization bound promoter DNA with properties similar to ExsA. Finally, we demonstrate that the activators of T3SS gene expression from Photorhabdus luminescens, Aeromonas hydrophila, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus are also sensitive to mutations that disrupt the ExsA consensus binding site.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Yersinia Type III Secretion System Master Regulator LcrF.J Bacteriol. 2015 Dec 7;198(4):604-14. doi: 10.1128/JB.00686-15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26644429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orientation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExsA monomers bound to promoter DNA and base-specific contacts with the P(exoT) promoter.J Bacteriol. 2012 May;194(10):2573-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.00107-12. Epub 2012 Mar 9. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22408167 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExsA DNA-Binding Activity by N-Hydroxybenzimidazoles.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Nov 16;60(2):766-76. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02242-15. Print 2016 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26574012 Free PMC article.
-
The distal ExsA-binding site in Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system promoters is the primary determinant for promoter-specific properties.J Bacteriol. 2012 May;194(10):2564-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.00106-12. Epub 2012 Mar 9. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22408165 Free PMC article.
-
Fitting Pieces into the Puzzle of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type III Secretion System Gene Expression.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jun 10;201(13):e00209-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00209-19. Print 2019 Jul 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31010903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Psychrotrophic Pseudomonas lundensis, a Non-aeruginosa Pseudomonad, Has a Type III Secretion System of the Ysc Family, Which Is Transcriptionally Active at 37°C.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0386921. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03869-21. Epub 2022 Feb 22. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35189702 Free PMC article.
-
Yersinia Type III Secretion System Master Regulator LcrF.J Bacteriol. 2015 Dec 7;198(4):604-14. doi: 10.1128/JB.00686-15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26644429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repression by the H-NS/YmoA histone-like protein complex enables IscR dependent regulation of the Yersinia T3SS.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jul 28;18(7):e1010321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010321. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35901167 Free PMC article.
-
The Yersinia pestis type III secretion system: expression, assembly and role in the evasion of host defenses.Immunol Res. 2013 Dec;57(1-3):237-45. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8454-3. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 24198067 Review.
-
The Transcriptional Regulator HlyU Positively Regulates Expression of exsA, Leading to Type III Secretion System 1 Activation in Vibrio parahaemolyticus.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jul 10;200(15):e00653-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00653-17. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29440251 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

