The FAK scaffold inhibitor C4 disrupts FAK-VEGFR-3 signaling and inhibits pancreatic cancer growth
- PMID: 24142503
- PMCID: PMC3858551
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1365
The FAK scaffold inhibitor C4 disrupts FAK-VEGFR-3 signaling and inhibits pancreatic cancer growth
Abstract
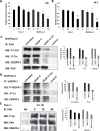
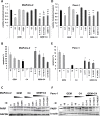
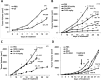
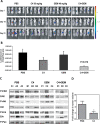
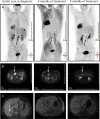
Even with successful surgical resection and perioperative chemotherapy and radiation, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) has a high incidence of recurrence. Tumor cell survival depends on activation of signaling pathways that suppress the apoptotic stimuli of invasion and metastasis. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a critical signaling molecule that has been implicated in tumor cell survival, invasion and metastasis. We have previously shown that FAK and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR-3) are overexpressed in cancer cells and physically interact to confer a significant survival advantage. We subsequently identified a novel small molecule inhibitor C4 that targeted the VEGFR-3-FAK site of interaction. In this study, we have shown that C4 disrupted the FAK-VEGFR-3 complexes in PDA cells. C4 treatment caused dose-dependent dephosphorylation and inactivation of the VEGFR-3 and FAK, reduction in cell viability and proliferation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in PDA cells. C4 increased the sensitivity of tumor cells to gemcitabine chemotherapy in vitro that lead to apoptosis at nanomolar concentrations of both drugs. C4 reduced tumor growth in vivo in subcutaneous and orthotopic murine models of PDA. The drug alone at low dose, decreased tumor growth; however, concomitant administration with low dose of gemcitabine had significant synergistic effect and led to 70% tumor reduction. Combination of C4 with gemcitabine had a prolonged cytostatic effect on tumor growth after treatment withdrawal. Finally, we report an anecdotal case of stage IV pancreatic cancer treated with gemcitabine in combination with C4 that showed a significant clinical response in primary tumor and complete clinical response in liver metastasis over an eight month period. Taken together, these results demonstrate that targeting the scaffolding function of FAK with a small-molecule FAK-VEGFR-3 inhibitor can be an effective therapeutic strategy against PDA.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A FAK scaffold inhibitor disrupts FAK and VEGFR-3 signaling and blocks melanoma growth by targeting both tumor and endothelial cells.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(16):2542-53. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2015.941760. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486195 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule chloropyramine hydrochloride (C4) targets the binding site of focal adhesion kinase and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 and suppresses breast cancer growth in vivo.J Med Chem. 2009 Aug 13;52(15):4716-24. doi: 10.1021/jm900159g. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19610651 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase by PF-562,271 inhibits the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer concomitant with altering the tumor microenvironment.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2135-45. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0261. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21903606 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of focal adhesion kinase inhibition in overcoming chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Future Med Chem. 2024 Feb;16(3):271-289. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2023-0234. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Future Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38269431 Review.
-
Development of focal adhesion kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Sep;11(7):638-42. doi: 10.2174/187152011796817628. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21787276 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of carbon ion beam and gemcitabine causes irreparable DNA damage and death of radioresistant pancreatic cancer stem-like cells in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 20;6(8):5517-35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3584. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25849939 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the C-terminal focal adhesion kinase scaffold in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Lett. 2014 Oct 28;353(2):281-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.032. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25067788 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Extra-Cellular Matrix-Tumor Cell Crosstalk for Anti-Cancer Therapy: Emerging Alternatives to Integrin Inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 22;10:1231. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01231. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32793493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chromosome 11q13.3 amplification associated lymph node metastasis is driven by miR-548k through modulating tumor microenvironment.Mol Cancer. 2018 Aug 21;17(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0871-4. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30131072 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic analysis of the FAK scaffold inhibitor C4 in dogs.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2016 Feb;41(1):55-67. doi: 10.1007/s13318-014-0233-6. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2016. PMID: 25377246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neesse A, Michl P, Frese KK, Feig C, Cook N, Jacobetz MA, Lolkema MP, Buchholz M, Olive KP, Gress TM, Tuveson DA. Stromal biology and therapy in pancreatic cancer. Gut. 2011;60(6):861–868. - PubMed
-
- Kim EJ, Simeone DM. Advances in pancreatic cancer. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 2011;27(5):460–466. 410.1097/MOG.1090b1013e328349e328331f. - PubMed
-
- Vaccaro V, Melisi D, Bria E, Cuppone F, Ciuffreda L, Pino MS, Gelibter A, Tortora G, Cognetti F, Milella M. Emerging pathways and future targets for the molecular therapy of pancreatic cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011;15(10):1183–1196. - PubMed
-
- Warsame R, Grothey A. Treatment options for advanced pancreatic cancer: a review. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy. 2012;12(10):1327–1336. - PubMed
-
- Garber K. Stromal depletion goes on trial in pancreatic cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(7):448–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

