Lipid emulsions enhance the norepinephrine-mediated reversal of local anesthetic-induced vasodilation at toxic doses
- PMID: 24142661
- PMCID: PMC3809849
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.6.1524
Lipid emulsions enhance the norepinephrine-mediated reversal of local anesthetic-induced vasodilation at toxic doses
Abstract
Purpose: Intravenous lipid emulsions have been used to treat the systemic toxicity of local anesthetics. The goal of this in vitro study was to examine the effects of lipid emulsions on the norepinephrine-mediated reversal of vasodilation induced by high doses of levobupivacaine, ropivacaine, and mepivacaine in isolated endothelium-denuded rat aorta, and to determine whether such effects are associated with the lipid solubility of local anesthetics.
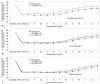
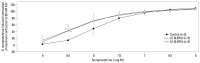
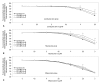
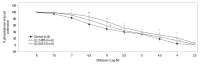
Materials and methods: The effects of lipid emulsions (0.30, 0.49, 1.40, and 2.61%) on norepinephrine concentration-responses in high-dose local anesthetic (6×10(-4) M levobupivacaine, 2×10(-3) M ropivacaine, and 7×10(-3) M mepivacaine)-induced vasodilation of isolated aorta precontracted with 60 mM KCl were assessed. The effects of lipid emulsions on local anesthetic- and diltiazem-induced vasodilation in isolated aorta precontracted with phenylephrine were also assessed.
Results: Lipid emulsions (0.30%) enhanced norepinephrine-induced contraction in levobupivacaine-induced vasodilation, whereas 1.40 and 2.61% lipid emulsions enhanced norepinephrine-induced contraction in both ropivacaine- and mepivacaine-induced vasodilation, respectively. Lipid emulsions (0.20, 0.49 and 1.40%) inhibited vasodilation induced by levobupivacaine and ropivacaine, whereas 1.40 and 2.61% lipid emulsions slightly attenuated mepivacaine (3×10(-3) M)-induced vasodilation. In addition, lipid emulsions attenuated diltiazem-induced vasodilation. Lipid emulsions enhanced norepinephrine-induced contraction in endothelium-denuded aorta without pretreatment with local anesthetics.
Conclusion: Taken together, these results suggest that lipid emulsions enhance the norepinephrine-mediated reversal of local anesthetic-induced vasodilation at toxic anesthetic doses and inhibit local anesthetic-induced vasodilation in a manner correlated with the lipid solubility of a particular local anesthetic.
Keywords: Lipid emulsion; local anesthetic-induced vasodilation; norepinephrine; systemic toxicity of local anesthetic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid Emulsion Inhibits Vasodilation Induced by a Toxic Dose of Bupivacaine via Attenuated Dephosphorylation of Myosin Phosphatase Target Subunit 1 in Isolated Rat Aorta.Int J Med Sci. 2015 Nov 5;12(12):958-67. doi: 10.7150/ijms.13299. eCollection 2015. Int J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26664257 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid emulsion-mediated reversal of toxic-dose aminoamide local anesthetic-induced vasodilation in isolated rat aorta.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013 Apr;64(4):353-9. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2013.64.4.353. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013. PMID: 23646246 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Acidification and Alkalinization on the Lipid Emulsion-Mediated Reversal of Toxic Dose Levobupivacaine-Induced Vasodilation in the Isolated Rat Aorta.Int J Med Sci. 2016 Jan 25;13(1):68-76. doi: 10.7150/ijms.13016. eCollection 2016. Int J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 26917987 Free PMC article.
-
The toxicity of local anesthetics: the place of ropivacaine and levobupivacaine.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2008 Oct;21(5):645-50. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e32830c214c. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2008. PMID: 18784493 Review.
-
Use of lipid emulsion to reverse local anesthetic-induced toxicity.Ann Pharmacother. 2007 Nov;41(11):1873-7. doi: 10.1345/aph.1K244. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Ann Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17895327 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid Emulsion Inhibits Vasodilation Induced by a Toxic Dose of Bupivacaine via Attenuated Dephosphorylation of Myosin Phosphatase Target Subunit 1 in Isolated Rat Aorta.Int J Med Sci. 2015 Nov 5;12(12):958-67. doi: 10.7150/ijms.13299. eCollection 2015. Int J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26664257 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid emulsion inhibits vasodilation induced by a toxic dose of bupivacaine by suppressing bupivacaine-induced PKC and CPI-17 dephosphorylation but has no effect on vasodilation induced by a toxic dose of mepivacaine.Korean J Pain. 2016 Oct;29(4):229-238. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.4.229. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Korean J Pain. 2016. PMID: 27738501 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Emulsion for Treating Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity.Int J Med Sci. 2018 May 14;15(7):713-722. doi: 10.7150/ijms.22643. eCollection 2018. Int J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29910676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential effects of short- and long-term bupivacaine treatment on α1-adrenoceptor-mediated contraction of isolated rat aorta rings and the reversal effect of lipid emulsion.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Aug;36(8):976-86. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.40. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 26073324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charbonneau H, Marcou TA, Mazoit JX, Zetlaoui PJ, Benhamou D. Early use of lipid emulsion to treat incipient mepivacaine intoxication. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009;34:277–278. - PubMed
-
- Schaeffer E, Rayaud L, Landy C, Boulland P, Favier JC. [Local anaesthetics intoxication, during ultrasound-guided axillary plexus block, treated by Intralipide] Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2010;29:929–930. - PubMed
-
- Sakai T, Manabe W, Kamitani T, Takeyama E, Nakano S. [Ropivacaine-induced late-onset systemic toxicity after transversus abdominis plane block under general anesthesia: successful reversal with 20% lipid emulsion] Masui. 2010;59:1502–1505. - PubMed
-
- Dix SK, Rosner GF, Nayar M, Harris JJ, Guglin ME, Winterfield JR, et al. Intractable cardiac arrest due to lidocaine toxicity successfully resuscitated with lipid emulsion. Crit Care Med. 2011;39:872–874. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg G, Ripper R, Feinstein DL, Hoffman W. Lipid emulsion infusion rescues dogs from bupivacaine-induced cardiac toxicity. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2003;28:198–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

