Radiotherapy influences local control in patients with desmoplastic melanoma
- PMID: 24142775
- PMCID: PMC4515972
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.28412
Radiotherapy influences local control in patients with desmoplastic melanoma
Abstract
Background: Desmoplastic melanoma may have a high risk of local recurrence after wide excision. The authors hypothesized that adjuvant radiotherapy (RT) would improve local control in patients with desmoplastic melanoma, resulting in at least a 10% absolute decrease in local recurrence rate.
Methods: A total of 277 patients from 1989 through 2010 who were treated for nonmetastatic desmoplastic melanoma by surgery with or without adjuvant RT were reviewed. Clinicopathologic and treatment variables were assessed with regard to their role in local control.
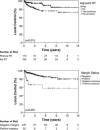
Results: A total of 113 patients (40.8%) received adjuvant RT. After a median follow-up of 43.1 months, adjuvant RT was found to be independently associated with improved local control on multivariable analysis (hazards ratio, 0.15; 95% confidence interval, 0.06-0.39 [P<.001]). Among 35 patients with positive resection margins, 14% who received RT developed a local recurrence versus 54% who did not (P=.004). In patients with negative resection margins, there was a trend (P=.09) toward improved local control with RT. In patients with negative resection margins and traditionally high-risk features, including a head and neck tumor location, a Breslow depth >4 mm, or a Clark level V tumor, RT was found to significantly improve local control (P< .05). The data from the current study would suggest that patients who would be good candidates for omitting RT included those with negative resection margins, a Breslow depth ≤ 4 mm, and either no perineural invasion present or a non-head and neck tumor location.
Conclusions: RT for desmoplastic melanoma was independently associated with improved local control. Patients with positive resection margins or deeper tumors appeared to benefit the most from RT, whereas selected low-risk patients can safely omit RT.
Keywords: control; desmoplastic; local neoplasm recurrence; melanoma; radiation; radiotherapy.
© 2013 American Cancer Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Increased clarity on the use of radiotherapy in the management of desmoplastic melanoma.Cancer. 2014 May 1;120(9):1315-8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28613. Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24877163 No abstract available.
References
-
- Quinn MJ, Crotty KA, Thompson JF, Coates AS, O'Brien CJ, McCarthy WH. Desmoplastic and desmoplastic neurotropic melanoma: experience with 280 patients. Cancer. 1998;83:1128–1135. - PubMed
-
- Busam KJ, Mujumdar U, Hummer AJ, et al. Cutaneous desmoplastic melanoma: reappraisal of morphologic heterogeneity and prognostic factors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:1518–1525. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins WG, Busam KJ, Ben-Porat L, et al. Desmoplastic melanoma: a pathologically and clinically distinct form of cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2005;12:207–213. - PubMed
-
- Smithers BM, McLeod GR, Little JH. Desmoplastic, neural transforming and neurotropic melanoma: a review of 45 cases. Aust N Z J Surg. 1990;60:967–972. - PubMed
-
- Jaroszewski DE, Pockaj BA, DiCaudo DJ, Bite U. The clinical behavior of desmoplastic melanoma. Am J Surg. 2001;182:590–595. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

