Retrospective revaluation of associative retroactive cue interference
- PMID: 24142799
- PMCID: PMC3975691
- DOI: 10.3758/s13420-013-0123-9
Retrospective revaluation of associative retroactive cue interference
Abstract
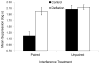
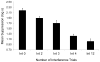
Two fear-conditioning experiments with rats assessed whether retrospective revaluation, which has been observed in cue competition (i.e., when compounded cues are followed with an outcome), can also be observed in retroactive cue interference (i.e., when different cues are reinforced in separate phases with the same outcome). Experiment 1 found that after inducing retroactive cue interference (i.e., X-outcome followed by A-outcome), nonreinforced presentations of the interfering cue (A) decreases interference with responding to the target cue (X), just as has been observed in retrospective revaluation experiments in cue competition. Using the opposite manipulation (i.e., adding reinforced presentations of A), Experiment 2 demonstrated that after inducing retroactive cue interference, additional reinforced presentations of the interfering cue (A) increases interference with responding to the target cue (X); alternatively stated, the amount of interference increases with the amount of training with the interfering cue. Thus, both types of retrospective revaluation occur in retroactive cue competition. The results are discussed in terms of the possibility that similar associative mechanisms underlie cue competition and cue interference.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Blocking is not 'pure' cue competition: Renewal-like effects in forward and backward blocking indicate contributions by associative cue interference.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2022 Apr;48(2):145-159. doi: 10.1037/xan0000315. Epub 2022 Feb 28. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2022. PMID: 35225640 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement and reduction of associative retroactive cue interference by training in multiple contexts.Learn Behav. 2014 Dec;42(4):318-29. doi: 10.3758/s13420-014-0149-7. Learn Behav. 2014. PMID: 25035103
-
Spontaneous recovery and ABC renewal from retroactive cue interference.Learn Behav. 2012 Mar;40(1):42-53. doi: 10.3758/s13420-011-0044-4. Learn Behav. 2012. PMID: 21881896
-
Retrospective revaluation: The phenomenon and its theoretical implications.Behav Processes. 2016 Feb;123:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Behav Processes. 2016. PMID: 26342855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Competition and facilitation in compound conditioning.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2017 Oct;43(4):303-314. doi: 10.1037/xan0000149. Epub 2017 Aug 10. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2017. PMID: 28795826 Review.
Cited by
-
Translations in Stimulus-Stimulus Pairing: Autoshaping of Learner Vocalizations.Perspect Behav Sci. 2019 Nov 25;43(1):57-103. doi: 10.1007/s40614-019-00228-9. eCollection 2020 Mar. Perspect Behav Sci. 2019. PMID: 32440645 Free PMC article.
-
Stepping back from 'persistence and relapse' to see the forest: Associative interference.Behav Processes. 2017 Aug;141(Pt 1):128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2017.03.014. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Behav Processes. 2017. PMID: 28323076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blocking is not 'pure' cue competition: Renewal-like effects in forward and backward blocking indicate contributions by associative cue interference.J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2022 Apr;48(2):145-159. doi: 10.1037/xan0000315. Epub 2022 Feb 28. J Exp Psychol Anim Learn Cogn. 2022. PMID: 35225640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amundson JC, Escobar M, Miller RR. Proactive interference between cues trained with a common outcome in first-order Pavlovian conditioning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes. 2003;29:311–322. - PubMed
-
- Balleine BW, Espinet A, González F. Perceptual learning enhances retrospective revaluation of conditioned flavor preferences in rats. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes. 2005;31:341–350. - PubMed
-
- Blaisdell AP, Gunther LM, Miller RR. Recovery from blocking achieved by extinguishing the blocking CS. Animal Learning & Behavior. 1999;27:63–76.
-
- Boddez Y, Baeyens F, Hermans D, Beckers T. The hide-and-seek of retrospective revaluation: Recovery from blocking is context dependent in human causal learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes. 2011;37:230–240. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME. Context, time, and memory retrieval in the interference paradigms of Pavlovian learning. Psychological Bulletin. 1993;114:80–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

