A comparative study of internal laser-assisted and conventional liposuction: a look at the influence of drugs and major surgery on laboratory postoperative values
- PMID: 24143076
- PMCID: PMC3798112
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S50828
A comparative study of internal laser-assisted and conventional liposuction: a look at the influence of drugs and major surgery on laboratory postoperative values
Abstract
Background: Liposuction is a type of aesthetic surgery that has been performed on humans for decades. There is not much literature addressing the subject matter of pre- and post-surgery blood parameters, although this information is rather interesting. Documentation on patients who received laser-assisted liposuction treatment is particularly scarce. Until now, there has been no literature showing values of platelets, lymphocytes, and neutrophils after liposuction.
Purpose: The aim of the work is to analyze and interpret values of platelets, lymphocytes and neutrophils in patient blood before and after liposuction, a surgery in which an extraordinarily large amount of potent drugs are used. Moreover, the aim is to compare values changes in patients of conventional and laser-assisted liposuction.
Material and methods: We evaluated standard blood samples in patients prior to and after liposuction. This paper covers the number of platelets, lymphocytes, and neutrophils. A total of 54 patients were examined. Moreover, we compared the change in postoperative values in laser-assisted liposuction patients with the change of values in conventional liposuction patients. A paired two-sided Student's t-test was used for statistical evaluation. P < 0.005 was acknowledged to be statistically significant.
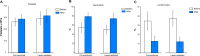
Results: Values of platelets were raised both in conventional and in laser-assisted liposuction patients, but this difference was statistically non-significant and levels of platelets were still normal and within the range of blood levels in healthy patients. Values of neutrophils rose by up to 79.49% ± 7.74% standard deviation (SD) and values of lymphocytes dropped by up to 12.68% ± 5.61% SD. The before/after variances of conventional tumescent local anesthesia liposuction and variations in laser-assisted liposuction were similar for all measured parameters; they also showed no statistically significant differences between before and after surgery. The mean value of total operation time without laser-assistance was 3 hours 42 minutes (± 57 minutes SD, range 2 hours 50 minutes to 5 hours 10 minutes). Surgeries with laser-assistance were on average 16 minutes shorter with a mean duration of 3 hours 26 minutes (± 45 minutes SD, range 2 hours 40 minutes to 4 hours 10 minutes). The difference was not statistically significant (P < 0.06). The mean value of aspirate volume for liposuctions performed without laser support was 2,618 mL (± 633.7 SD, range 700 mL to 3,500 mL). Mean aspirate volume for liposuctions with laser assistance was increased by up to 61 mL (2,677 mL ± 499.5 SD, range 1,800 mL to 3,500 mL). The difference was not statistically significant (P < 0.71).
Conclusion: We conclude that conventional liposuction and laser-assisted liposuction have a similar influence on platelets, lymphocytes, and neutrophils in patients. Moreover, laser-assisted liposuction seems to be less time consuming than conventional liposuction.
Keywords: laser; lipolysis; liposuction; lymphocytes; neutrophils; platelets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
1,000 consecutive cases of laser-assisted liposuction and suction-assisted lipectomy managed with local anesthesia.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012 Aug;36(4):795-802. doi: 10.1007/s00266-012-9885-2. Epub 2012 Mar 24. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012. PMID: 22447150
-
1000 Consecutive Cases of Laser-Assisted Liposuction Utilizing the 1440 nm Wavelength Nd:YAG Laser: Assessing the Safety and Efficacy.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2018 Feb;42(1):9-12. doi: 10.1007/s00266-017-0964-2. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2018. PMID: 28916849
-
Radiofrequency-assisted liposuction device for body contouring: 97 patients under local anesthesia.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012 Aug;36(4):767-79. doi: 10.1007/s00266-011-9846-1. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2012. PMID: 22466060
-
Laser-assisted lipolysis: a review.Dermatol Surg. 2012 Feb;38(2):155-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02168.x. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Dermatol Surg. 2012. PMID: 22093156 Review.
-
Safety of tumescent and laser-assisted liposuction: review of the literature.J Drugs Dermatol. 2011 Dec;10(12):1363-9. J Drugs Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 22134559 Review.
References
-
- Klein JA. The Tumescent technique for liposuction surgery. Am J Cosmet Surg. 1987;4:263–267.
-
- Hanke CW, Bernstein G, Bullock S. Safety of tumescent liposuction in 15,336 patients. National survey results. Dermatol Surg. 1995;21(5):459–462. - PubMed
-
- Karmo FR, Milan MF, Silbergleit A. Blood loss in major liposuction procedures: a comparison study using suction-assisted versus ultrasonically assisted lipoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;108(1):241–247. discussion 248–249. - PubMed
-
- Peterson AF, Przylipiak J, Peterson M. Influence of laser-supported liposuction on hemoglobin, hematocrit, and erythrocyte values in patient’s blood. Eur J Plast Surg. 2009;32(6):283–286.
-
- Schafer AI. Thrombocytosis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(12):1211–1219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources