Characterizing brain structures and remodeling after TBI based on information content, diffusion entropy
- PMID: 24143186
- PMCID: PMC3797055
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076343
Characterizing brain structures and remodeling after TBI based on information content, diffusion entropy
Abstract
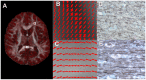
Background: To overcome the limitations of conventional diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging resulting from the assumption of a Gaussian diffusion model for characterizing voxels containing multiple axonal orientations, Shannon's entropy was employed to evaluate white matter structure in human brain and in brain remodeling after traumatic brain injury (TBI) in a rat.
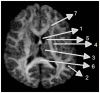
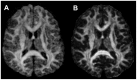
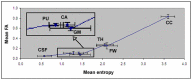
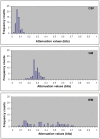
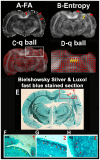
Methods: Thirteen healthy subjects were investigated using a Q-ball based DTI data sampling scheme. FA and entropy values were measured in white matter bundles, white matter fiber crossing areas, different gray matter (GM) regions and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Axonal densities' from the same regions of interest (ROIs) were evaluated in Bielschowsky and Luxol fast blue stained autopsy (n = 30) brain sections by light microscopy. As a case demonstration, a Wistar rat subjected to TBI and treated with bone marrow stromal cells (MSC) 1 week after TBI was employed to illustrate the superior ability of entropy over FA in detecting reorganized crossing axonal bundles as confirmed by histological analysis with Bielschowsky and Luxol fast blue staining.
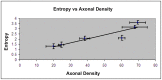
Results: Unlike FA, entropy was less affected by axonal orientation and more affected by axonal density. A significant agreement (r = 0.91) was detected between entropy values from in vivo human brain and histologically measured axonal density from post mortum from the same brain structures. The MSC treated TBI rat demonstrated that the entropy approach is superior to FA in detecting axonal remodeling after injury. Compared with FA, entropy detected new axonal remodeling regions with crossing axons, confirmed with immunohistological staining.
Conclusions: Entropy measurement is more effective in distinguishing axonal remodeling after injury, when compared with FA. Entropy is also more sensitive to axonal density than axonal orientation, and thus may provide a more accurate reflection of axonal changes that occur in neurological injury and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diffusion-Derived Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measures of Longitudinal Microstructural Remodeling Induced by Marrow Stromal Cell Therapy after Traumatic Brain Injury.J Neurotrauma. 2017 Jan 1;34(1):182-191. doi: 10.1089/neu.2015.4315. Epub 2016 May 13. J Neurotrauma. 2017. PMID: 26993214 Free PMC article.
-
MRI evaluation of axonal reorganization after bone marrow stromal cell treatment of traumatic brain injury.NMR Biomed. 2011 Nov;24(9):1119-28. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1667. Epub 2011 Mar 23. NMR Biomed. 2011. PMID: 21432927 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging detects clinically important axonal damage after mild traumatic brain injury: a pilot study.J Neurotrauma. 2007 Sep;24(9):1447-59. doi: 10.1089/neu.2007.0241. J Neurotrauma. 2007. PMID: 17892407
-
Traumatic brain injury, major depression, and diffusion tensor imaging: making connections.Brain Res Rev. 2010 Sep;64(1):213-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 11. Brain Res Rev. 2010. PMID: 20388528 Review.
-
White matter involvement after TBI: Clues to axon and myelin repair capacity.Exp Neurol. 2016 Jan;275 Pt 3:328-333. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 25697845 Review.
Cited by
-
White Matter Injury in Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Cell Transplant. 2019 Jan;28(1):26-35. doi: 10.1177/0963689718812054. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30442028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
White Matter Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Front Neurol. 2021 Jun 10;12:562090. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.562090. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34177751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
White matter changes after stroke in type 2 diabetic rats measured by diffusion magnetic resonance imaging.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017 Jan;37(1):241-251. doi: 10.1177/0271678X15622464. Epub 2015 Dec 18. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017. PMID: 26685128 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging as a prognostic biomarker for motor recovery and rehabilitation after stroke.Neuroradiology. 2017 Apr;59(4):343-351. doi: 10.1007/s00234-017-1816-0. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Neuroradiology. 2017. PMID: 28293701 Review.
-
White matter changes in patients with mild traumatic brain injury: MRI perspective.Concussion. 2017 Mar 22;2(2):CNC35. doi: 10.2217/cnc-2016-0028. eCollection 2017 Jun. Concussion. 2017. PMID: 30202576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B 103: 247–254. - PubMed
-
- Horsfield MA, Larsson HB, Jones DK, Gass A (1998) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64 Suppl 1S80–84. - PubMed
-
- Zivadinov R, Stosic M, Cox JL, Ramasamy DP, Dwyer MG (2008) The place of conventional MRI and newly emerging MRI techniques in monitoring different aspects of treatment outcome. J Neurol 255 Suppl 161–74. - PubMed
-
- Ellis CM, Simmons A, Jones DK, Bland J, Dawson JM, et al. (1999) Diffusion tensor MRI assesses corticospinal tract damage in ALS. Neurology 53: 1051–1058. - PubMed
-
- Jones DK, Lythgoe D, Horsfield MA, Simmons A, Williams SC, et al. (1999) Characterization of white matter damage in ischemic leukoaraiosis with diffusion tensor MRI. Stroke 30: 393–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

