Structural and mechanistic insight into DNA unwinding by Deinococcus radiodurans UvrD
- PMID: 24143224
- PMCID: PMC3797037
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077364
Structural and mechanistic insight into DNA unwinding by Deinococcus radiodurans UvrD
Abstract
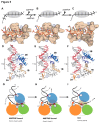
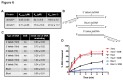
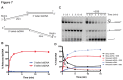
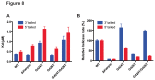
DNA helicases are responsible for unwinding the duplex DNA, a key step in many biological processes. UvrD is a DNA helicase involved in several DNA repair pathways. We report here crystal structures of Deinococcus radiodurans UvrD (drUvrD) in complex with DNA in different nucleotide-free and bound states. These structures provide us with three distinct snapshots of drUvrD in action and for the first time trap a DNA helicase undergoing a large-scale spiral movement around duplexed DNA. Our structural data also improve our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that regulate DNA unwinding by Superfamily 1A (SF1A) helicases. Our biochemical data reveal that drUvrD is a DNA-stimulated ATPase, can translocate along ssDNA in the 3'-5' direction and shows ATP-dependent 3'-5', and surprisingly also, 5'-3' helicase activity. Interestingly, we find that these translocase and helicase activities of drUvrD are modulated by the ssDNA binding protein. Analysis of drUvrD mutants indicate that the conserved β-hairpin structure of drUvrD that functions as a separation pin is critical for both drUvrD's 3'-5' and 5'-3' helicase activities, whereas the GIG motif of drUvrD involved in binding to the DNA duplex is essential for the 5'-3' helicase activity only. These special features of drUvrD may reflect its involvement in a wide range of DNA repair processes in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanistic basis of 5'-3' translocation in SF1B helicases.Cell. 2009 May 29;137(5):849-59. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.036. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19490894
-
An oligomeric form of E. coli UvrD is required for optimal helicase activity.J Mol Biol. 1999 Nov 5;293(4):815-34. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3185. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10543970
-
Mechanism of ATP-dependent translocation of E.coli UvrD monomers along single-stranded DNA.J Mol Biol. 2004 Dec 10;344(5):1287-309. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.10.005. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15561144
-
Non-hexameric DNA helicases and translocases: mechanisms and regulation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;9(5):391-401. doi: 10.1038/nrm2394. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18414490 Review.
-
Insights into the Dynamics and Helicase Activity of RecD2 of Deinococcus radiodurans during DNA Repair: A Single-Molecule Perspective.J Phys Chem B. 2023 May 25;127(20):4351-4363. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c00778. Epub 2023 May 10. J Phys Chem B. 2023. PMID: 37163679 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis of the XPB helicase-Bax1 nuclease complex interacting with the repair bubble DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Nov 18;48(20):11695-11705. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa801. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32986831 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insight into the PCNA-binding mode of FBH1.Structure. 2023 May 4;31(5):511-517.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2023.03.004. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Structure. 2023. PMID: 36990095 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional insights into the activation of the dual incision activity of UvrC, a key player in bacterial NER.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Apr 11;51(6):2931-2949. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad108. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36869664 Free PMC article.
-
F-box DNA Helicase 1 (FBH1) Contributes to the Destabilization of DNA Damage Repair Machinery in Human Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 6;15(18):4439. doi: 10.3390/cancers15184439. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760409 Free PMC article.
-
A Decade of Biochemical and Structural Studies of the DNA Repair Machinery of Deinococcus radiodurans: Major Findings, Functional and Mechanistic Insight and Challenges.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016 Apr 7;14:168-176. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2016.04.001. eCollection 2016. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016. PMID: 27924191 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gorbalenya AE, Koonin EV (1993) Helicases: amino acid sequence comparisons and structure-function relationships. Curr Opin Struct Biol 3: 419-429. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(05)80116-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

