Choline plasmalogens isolated from swine liver inhibit hepatoma cell proliferation associated with caveolin-1/Akt signaling
- PMID: 24143228
- PMCID: PMC3797038
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077387
Choline plasmalogens isolated from swine liver inhibit hepatoma cell proliferation associated with caveolin-1/Akt signaling
Abstract
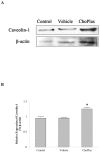
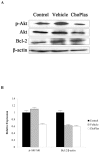
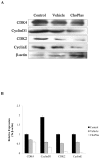
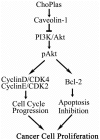
Plasmalogens play multiple roles in the structures of biological membranes, cell membrane lipid homeostasis and human diseases. We report the isolation and identification of choline plasmalogens (ChoPlas) from swine liver by high performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/MS. The growth and viability of hepatoma cells (CBRH7919, HepG2 and SMMC7721) was determined following ChoPlas treatment comparing with that of human normal immortal cell lines (HL7702). Result indicated that ChoPlas inhibited hepatoma cell proliferation with an optimal concentration and time of 25 μmol/L and 24 h. To better understand the mechanism of the ChoPlas-induced inhibition of hepatoma cell proliferation, Caveolin-1 and PI3K/Akt pathway signals, including total Akt, phospho-Akt(pAkt) and Bcl-2 expression in CBRH7919 cells, were determined by western blot. ChoPlas treatment increased Caveolin-1 expression and reduced the expression of phospho-Akt (pAkt) and Bcl-2, downstream targets of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Further cell cycle analysis showed that ChoPlas treatment induced G1 and G1/S phase transition cell cycle arrest. The expression of essential cell cycle regulatory proteins involved in the G1 and G1/S phase transitions, cyclin D, CDK4, cyclin E and CDK2, were also analyzed by western blot. ChoPlas reduced CDK4, cyclin E and CDK2 expression. Taken together, the results indicate that swine liver-derived natural ChoPlas inhibits hepatoma cell proliferation associated with Caveolin-1 and PI3K/Akt signals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anti-liver cancer effect and the mechanism of arsenic sulfide in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;83(3):519-530. doi: 10.1007/s00280-018-3755-9. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30542770
-
Hespintor Negative Regulation of PI3K/Akt Pathway Induces Cell Cycle Arrest of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2024 Dec;178(2):237-243. doi: 10.1007/s10517-025-06314-0. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39762705
-
AKT signalling and mitochondrial pathways are involved in mushroom polysaccharide-induced apoptosis and G1 or S phase arrest in human hepatoma cells.Food Chem. 2013 Jun 15;138(4):2130-9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.047. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 23497867
-
The antiproliferative effect of spectinabilins from Streptomyces spectabilis on hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Dec;93:103311. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103311. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31586709
-
Cyclin G1 expands liver tumor-initiating cells by Sox2 induction via Akt/mTOR signaling.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Sep;12(9):1796-804. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0099. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23804702
Cited by
-
Plasmalogen lipids: functional mechanism and their involvement in gastrointestinal cancer.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Mar 7;17(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0685-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29514688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal Intervention Strategy Targeting Myeloid Cells to Improve Hepatic Immunity during Hepatocarcinoma Development.Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 6;9(11):1633. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111633. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829862 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 regulation of Sp1 controls production of the antifibrotic protein follistatin in kidney mesangial cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Apr 17;17(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0351-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 30995923 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of endogenous plasmalogens by genetic ablation of lysoplasmalogenase (Tmem86b) in mice.J Lipid Res. 2025 May;66(5):100808. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100808. Epub 2025 Apr 17. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 40245986 Free PMC article.
-
The ether lipid precursor hexadecylglycerol stimulates the release and changes the composition of exosomes derived from PC-3 cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 13;290(7):4225-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.593962. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25519911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wood PL, Khan MA, Smith T, Ehrmantraut G, Jin W et al. ( 2011. ) In vitro and in vivo plasmalogen replacement evaluations in rhizomelic chrondrodysplasia punctata and Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease using PPI-1011, an ether lipid plasmalogen precursor. Lipids Health Dis 10: 182. doi:10.1186/1476-511X-10-182. PubMed: 22008564. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

