Differential activation of Wnt-β-catenin pathway in triple negative breast cancer increases MMP7 in a PTEN dependent manner
- PMID: 24143235
- PMCID: PMC3797090
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077425
Differential activation of Wnt-β-catenin pathway in triple negative breast cancer increases MMP7 in a PTEN dependent manner
Abstract
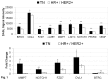
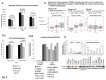
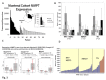
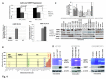
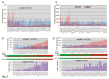
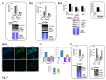
Mutations of genes in tumor cells of Triple Negative subset of Breast Cancer (TNBC) deregulate pathways of signal transduction. The loss of tumor suppressor gene PTEN is the most common first event associated with basal-like subtype (Martins, De, Almendro, Gonen, and Park, 2012). Here we report for the first time that the functional upregulation of secreted-MMP7, a transcriptional target of Wnt-β-catenin signature pathway in TNBC is associated to the loss of PTEN. We identified differential expression of mRNAs in several key-components genes, and transcriptional target genes of the Wnt-β-catenin pathway (WP), including beta-catenin, FZD7, DVL1, MMP7, c-MYC, BIRC5, CD44, PPARD, c-MET, and NOTCH1 in FFPE tumors samples from TNBC patients of two independent cohorts. A similar differential upregulation of mRNA/protein for beta-catenin, the functional readout of WP, and for MMP7, a transcriptional target gene of beta-catenin was observed in TNBC cell line models. Genetic or pharmacological attenuation of beta-catenin by SiRNA or WP modulators (XAV939 and sulindac sulfide) and pharmacological mimicking of PTEN following LY294002 treatment downregulated MMP7 levels as well as enzymatic function of the secreted MMP7 in MMP7 positive PTEN-null TNBC cells. Patient data revealed that MMP7 mRNA was high in only a subpopulation of TNBC, and this subpopulation was characterized by a concurrent low expression of PTEN mRNA. In cell lines, a high expression of casein-zymograph-positive MMP7 was distinguished by an absence of functional PTEN. A similar inverse relationship between MMP7 and PTEN mRNA levels was observed in the PAM50 data set (a correlation coefficient of -0.54). The PAM50 subtype and outcome data revealed that the high MMP7 group had low pCR (25%) and High Rd (74%) in clinical stage T3 pathologic response in contrast to the high pCR (40%) and low residual disease (RD) (60%) of the low MMP7 group.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Wnt-beta-catenin pathway signals metastasis-associated tumor cell phenotypes in triple negative breast cancers.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):43124-43149. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8988. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27281609 Free PMC article.
-
RAC1 GTP-ase signals Wnt-beta-catenin pathway mediated integrin-directed metastasis-associated tumor cell phenotypes in triple negative breast cancers.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3072-3103. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13618. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27902969 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling in triple negative breast cancer is associated with metastasis.BMC Cancer. 2013 Nov 10;13:537. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-537. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24209998 Free PMC article.
-
FOXC1-induced non-canonical WNT5A-MMP7 signaling regulates invasiveness in triple-negative breast cancer.Oncogene. 2018 Mar;37(10):1399-1408. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0021-2. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29249801 Free PMC article.
-
A subgroup of microRNAs defines PTEN-deficient, triple-negative breast cancer patients with poorest prognosis and alterations in RB1, MYC, and Wnt signaling.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 31;21(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1098-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30704524 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enriched transcription factor signatures in triple negative breast cancer indicates possible targeted therapies with existing drugs.Meta Gene. 2015 May 15;4:129-41. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2015.04.002. eCollection 2015 Jun. Meta Gene. 2015. PMID: 26005638 Free PMC article.
-
MYC-xing it up with PIK3CA mutation and resistance to PI3K inhibitors: summit of two giants in breast cancers.Am J Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 15;5(1):1-19. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25628917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HER2 in stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity of breast cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 May;21(5):539-555. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1961-x. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30306401 Review.
-
Nanotechnological Approaches for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(10):781-799. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220608144551. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 35676850 Review.
-
Endocrine Therapy of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Cells: Early Differential Effects on Stem Cell Markers.Front Oncol. 2017 Sep 4;7:184. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00184. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28929082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bilici A, Arslan C, Altundag K (2012) Promising therapeutic options in triple-negative breast cancer. Journal of BUON 17: 209-222. - PubMed
-
- Dreyer G, Vandorpe T, Smeets A, Forceville K, Brouwers B, et al. (2013) Triple negative breast cancer: clinical characteristics in the different histological subtypes. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland). - PubMed
-
- Carey LA (2011) Directed therapy of subtypes of triple-negative breast cancer. Oncologist 16 Suppl 1: 71-78. - PubMed
-
- Moulder SL (2010) Does the PI3K pathway play a role in basal breast cancer? Clinical Breast Cancer 10: S66-S71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

