Pancreatic fluid collection drainage by endoscopic ultrasound: an update
- PMID: 24143313
- PMCID: PMC3797936
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2013.46.5.506
Pancreatic fluid collection drainage by endoscopic ultrasound: an update
Abstract
Endoscopic management of symptomatic pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) is now considered to be first line therapy. Expanded use of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) techniques has resulted in increased applicability, safety, and efficacy of endoscopic transluminal PFC drainage. Steps include EUS-guided trangastric or transduodenal fistula creation into the PFC followed by stent placement or nasocystic drain deployment in order to decompress the collection. With the remarkable improvement in the available accessories and stents and development of exchange free access device; EUS drainage techniques have become simpler and less time consuming. The use of self-expandable metal stents with modifications to drain PFC has helped in overcoming some previously encountered challenges. PFCs considered suitable for endoscopic drainage include collection present for greater than 4 weeks, possessing a well-formed wall, position accessible endoscopically and located within 1 cm of the duodenal or gastric walls. Indications for EUS-guided drainage have been increasing which include unusual location of the collection, small window of entry, nonbulging collections, coagulopathy, intervening varices, failed conventional transmural drainage, indeterminate adherence of PFC to the luminal wall or suspicion of malignancy. In this article, we present a review of literature to date and discuss the recent developments in EUS-guided PFC drainage.
Keywords: Endosonography; Nonbulging pancreatic fluid collections; Pancreatic fluid collections; Pancreatic pseudocyst.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Michel Kahaleh has received grant support from Boston Scientific, Fujinon, EMcison, Xlumena Inc., MaunaKea, and MI Tech. He is a consultant for Xlumena Inc.
Figures
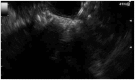
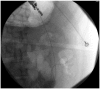

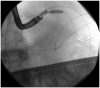
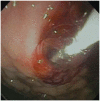

Similar articles
-
Pancreatic fluid collection drainage by endoscopic ultrasound: new perspectives.Endosc Ultrasound. 2012 Jul;1(2):61-8. doi: 10.7178/eus.02.002. Endosc Ultrasound. 2012. PMID: 24949339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided transluminal drainage for peripancreatic fluid collections: where are we now?Gut Liver. 2014 Jul;8(4):341-55. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2014.8.4.341. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Gut Liver. 2014. PMID: 25071899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Nov 16;4(11):479-88. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i11.479. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012. PMID: 23189219 Free PMC article.
-
Role of EUS in drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections not amenable for endoscopic transmural drainage.Gastrointest Endosc. 2007 Dec;66(6):1107-19. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2007.03.1027. Epub 2007 Sep 24. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007. PMID: 17892874
-
Endoscopic ultrasound guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections: Assessment of the procedure, technical details and review of the literature.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Apr 16;7(4):354-63. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i4.354. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25901214 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous Closure of a Large Transmural Gastric Defect After Removal of a Migrated AXIOS Stent.ACG Case Rep J. 2019 Mar 13;6(3):1-3. doi: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000033. eCollection 2019 Mar. ACG Case Rep J. 2019. PMID: 31620499 Free PMC article.
-
Coaxial Double-Pigtail Stent Placement: A Simple Solution to Decrease Bleeding Risk Associated With Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent?Cureus. 2021 Jun 28;13(6):e15981. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15981. eCollection 2021 Jun. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34336472 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Lumen-Apposing Metal Stents in Management of Pancreatic Fluid Collections: Are They Better Than Plastic Stents? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Feb;63(2):289-301. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4851-0. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29282638
-
A multi-institutional consensus on how to perform endoscopic ultrasound-guided peri-pancreatic fluid collection drainage and endoscopic necrosectomy.Endosc Ultrasound. 2017 Sep-Oct;6(5):285-291. doi: 10.4103/eus.eus_85_17. Endosc Ultrasound. 2017. PMID: 29063871 Free PMC article.
-
Do lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) improve treatment outcomes of walled-off pancreatic necrosis over plastic stents using dual-modality drainage?Endosc Int Open. 2017 Nov;5(11):E1052-E1059. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-111794. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Endosc Int Open. 2017. PMID: 29090245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baron TH, Thaggard WG, Morgan DE, Stanley RJ. Endoscopic therapy for organized pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:755–764. - PubMed
-
- Baillie J. Pancreatic pseudocysts (Part I) Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:873–879. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis M, Delhaye M, Chamlou R, et al. Endoscopic therapy for main pancreatic-duct rupture after Silastic-ring vertical gastroplasty. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;62:143–151. - PubMed
-
- Klöppel G. Pseudocysts and other non-neoplastic cysts of the pancreas. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000;17:7–15. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

