A trial of Scrambler therapy in the treatment of cancer pain syndromes and chronic chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
- PMID: 24143893
- PMCID: PMC4378693
- DOI: 10.3109/15360288.2013.847519
A trial of Scrambler therapy in the treatment of cancer pain syndromes and chronic chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
Abstract
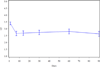
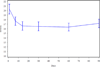
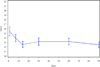
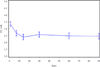
Neuropathic pain is common among cancer patients and often difficult to treat. This study used Scrambler therapy, a patient-specific electrocutaneous nerve stimulation device, to treat cancer patients with pain. Patients received Scrambler therapy for 10 sessions (one daily) over a two-week period. The primary outcome was changed in pain numerical rating scale (NRS) at one month; secondary outcomes were changes in the Brief Pain Inventory and European Organization for Treatment and Cancer QLC-CIPN-20(EORTC CIPN-20), over time. Thirty-nine patients, mean age 56.5 yr, 16 men and 23 women, were treated over an 18-month period for an average of 9.3 days each. The "now" pain scores reduced from 6.6 before treatment to 4.5 at 14 days, 4.6, 4.8, and 4.6 at 1, 2, and 3 months, respectively (p < 0.001). Clinically important and statistically significant improvements were seen in average, least, and worst pain; BPI interference with life scores, and motor and sensory scales on the EORTC CIPN-20. No adverse effects were observed. In this single arm trial, Scrambler therapy appeared to relieve cancer-associated chronic neuropathic pain both acutely and chronically, and provided sustained improvements in many indicators of quality of life.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The impact of scrambler therapy on pain and quality of life for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A pilot study.Pain Pract. 2024 Jun;24(5):749-759. doi: 10.1111/papr.13355. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Pain Pract. 2024. PMID: 38418433
-
Scrambler therapy for chemotherapy neuropathy: a randomized phase II pilot trial.Support Care Cancer. 2020 Mar;28(3):1183-1197. doi: 10.1007/s00520-019-04881-3. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Support Care Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31209630 Clinical Trial.
-
Pilot evaluation of Scrambler therapy for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.Support Care Cancer. 2015 Apr;23(4):943-51. doi: 10.1007/s00520-014-2424-8. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Support Care Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25245776 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment related peripheral neuropathies.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2014 Dec;15(4):567-80. doi: 10.1007/s11864-014-0303-7. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25119581 Review.
-
Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Systematic Review and Recommendations.Pain Physician. 2018 Nov;21(6):571-592. Pain Physician. 2018. PMID: 30508986
Cited by
-
Scrambler Therapy Enhances Quality of Life in Cancer Patients in a Palliative Care Setting: A Randomised Controlled Trial.Indian J Palliat Care. 2022 Jul-Sep;28(3):287-294. doi: 10.25259/IJPC_94_2021. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Indian J Palliat Care. 2022. PMID: 36072252 Free PMC article.
-
Updates in the Treatment of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022 Jan;23(1):29-42. doi: 10.1007/s11864-021-00926-0. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35167004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilot evaluation of scrambler therapy for pain induced by bone and visceral metastases and refractory to standard therapies.Support Care Cancer. 2016 Apr;24(4):1649-54. doi: 10.1007/s00520-015-2952-x. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Support Care Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26408323
-
Scrambler Therapy for the management of chronic pain.Support Care Cancer. 2016 Jun;24(6):2807-14. doi: 10.1007/s00520-016-3177-3. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Support Care Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27041741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in children and adolescent cancer patients.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Oct 14;9:1015746. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1015746. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36310587 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Botez SA, Herrmann DN. Sensory neuropathies, from symptoms to treatment. Curr Opin Neurol. 2010 Oct;23(5):502–508. - PubMed
-
- Finnerup NB, Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2010 Sep;150(3):573–581. - PubMed
-
- Marineo G. Untreatable pain resulting from abdominal cancer: new hope from biophysics? JOP. 2003 Jan;4(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Sabato AF, Marineo G, Gatti A. Calmare therapy. Minerva Anestesiol. 2005 Jul-Aug;71(7–8):479–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
