Crystallization of G protein-coupled receptors
- PMID: 24143992
- PMCID: PMC4605854
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-408143-7.00024-4
Crystallization of G protein-coupled receptors
Abstract
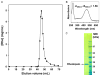
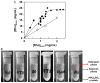
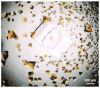
Oligomerization is one of several mechanisms that can regulate the activity of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), but little is known about the structure of GPCR oligomers. Crystallography and NMR are the only methods able to reveal the details of receptor-receptor interactions at an atomic level, and several GPCR homodimers already have been described from crystal structures. Two clusters of symmetric interfaces have been identified from these structures that concur with biochemical data, one involving helices I, II, and VIII and the other formed mainly by helices V and VI. In this chapter, we describe the protocols used in our laboratory for the crystallization of rhodopsin and the β2-adrenergic receptor (β2-AR). For bovine rhodopsin, we developed a new purification strategy including a (NH4)2SO4-induced phase separation that proved essential to obtain crystals of photoactivated rhodopsin containing parallel dimers. Crystallization of native bovine rhodopsin was achieved by the classic vapor-diffusion technique. For β2-AR, we developed a purification strategy based on previously published protocols employing a lipidic cubic phase to obtain diffracting crystals of a β2-AR/T4-lysozyme chimera bound to the antagonist carazolol.
Keywords: Ammonium sulfate; Crystallization; G protein-coupled receptor; Lipidic cubic phase; Purification; Rhodopsin; β2-Adrenergic receptor.
copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-resolution crystal structure of an engineered human beta2-adrenergic G protein-coupled receptor.Science. 2007 Nov 23;318(5854):1258-65. doi: 10.1126/science.1150577. Epub 2007 Oct 25. Science. 2007. PMID: 17962520 Free PMC article.
-
N-terminal T4 lysozyme fusion facilitates crystallization of a G protein coupled receptor.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046039. Epub 2012 Oct 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056231 Free PMC article.
-
Improvements in G protein-coupled receptor purification yield light stable rhodopsin crystals.J Struct Biol. 2006 Dec;156(3):497-504. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2006.05.003. Epub 2006 Jun 2. J Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16837211
-
Beyond rhodopsin: G protein-coupled receptor structure and modeling incorporating the beta2-adrenergic and adenosine A(2A) crystal structures.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;672:359-86. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-839-3_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20838977 Review.
-
X-ray structure breakthroughs in the GPCR transmembrane region.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jul 1;78(1):11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.02.012. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19447219 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential stability of the crystallographic interfaces of mu- and kappa-opioid receptors.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e90694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090694. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24651466 Free PMC article.
-
Photocyclic behavior of rhodopsin induced by an atypical isomerization mechanism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 28;114(13):E2608-E2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1617446114. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28289214 Free PMC article.
-
NeoR, a near-infrared absorbing rhodopsin.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 10;11(1):5682. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19375-8. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33173168 Free PMC article.
-
Chemistry and biology of the initial steps in vision: the Friedenwald lecture.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Oct 22;55(10):6651-72. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-15502. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 25338686 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-Mediated Oligomerization of G Protein Coupled Receptors and Its Implications for GPCR Function.Front Physiol. 2016 Oct 25;7:494. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00494. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27826255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexandrov AI, Mileni M, Chien EY, Hanson MA, Stevens RC. Micro-scale fluorescent thermal stability assay for membrane proteins. Structure. 2008;16(3):351–359. - PubMed
-
- Cherezov V, Caffrey M. Membrane protein crystallization in lipidic mesophases. A mechanism study using X-ray microdiffraction. Faraday Discussions. 2007;136:195–212. discussion 213–129. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

