Variable copy number of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) predicts worse prognosis in advanced gastric cancer patients
- PMID: 24144008
- PMCID: PMC4015835
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-173
Variable copy number of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) predicts worse prognosis in advanced gastric cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Change of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number is widely reported in various human cancers, including gastric cancer, and is considered to be an important hallmark of cancers. However, there is remarkably little consensus on the value of variable mtDNA content in the prognostic evaluation of this cancer.
Methods: Using real-time quantitative PCR approach, we examined mtDNA copy number in a cohort of gastric cancers and normal gastric tissues, and explored the association of variable mtDNA content with clinical outcomes of gastric cancer patients.
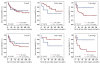
Results: Our data showed that the majority of gastric cancer patients had low mtDNA content as compared to control subjects although the relative mean mtDNA content was higher in the former than the latter. Moreover, we found that variable mtDNA content was strongly associated with lymph node metastasis and cancer-related death of the patients with late-stage tumors. Notably, variable mtDNA content did not affect overall survival of gastric cancer patients, however, we found that increased mtDNA content was associated with poor survival in the patients with late-stage tumors.
Conclusion: In this study, we demonstrated that variable mtDNA content markedly increased the risk of lymph node metastasis and high mortality of the patients with late-stage tumors. Additionally, we found a strong link between increased mtDNA content and worse survival of the patients with late-stage tumors. Taken together, variable mtDNA content may be a valuable poor prognostic factor for advanced gastric cancer patients.
Virtual slides: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/1344721463103353.
Figures

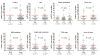
Similar articles
-
Low copy number of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) predicts worse prognosis in early-stage laryngeal cancer patients.Diagn Pathol. 2014 Feb 5;9:28. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-28. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24499477 Free PMC article.
-
Is mitochondrial DNA copy number associated with clinical characteristics and prognosis in gastric cancer?Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(1):87-90. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.1.87. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25640396
-
Mitochondrial DNA copy number and risk of gastric cancer: a report from the Shanghai Women's Health Study.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011 Sep;20(9):1944-9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0379. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011. PMID: 21784958 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic alterations in mitochondrial DNA and mitochondrial dysfunction in gastric cancer progression.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 14;20(14):3950-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3950. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24744584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives on new biomarkers in gastric cancer: diagnostic and prognostic applications.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Sep 7;20(33):11574-85. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11574. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25206265 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decrease of MtDNA copy number affects mitochondrial function and involves in the pathological consequences of ischaemic stroke.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Aug;26(15):4157-4168. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17262. Epub 2022 Jul 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35791521 Free PMC article.
-
Low mitochondrial DNA copy number induces chemotherapy resistance via epithelial-mesenchymal transition by DNA methylation in esophageal squamous cancer cells.J Transl Med. 2022 Aug 29;20(1):383. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03594-2. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36038893 Free PMC article.
-
Insights regarding mitochondrial DNA copy number alterations in human cancer (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 Aug;50(2):104. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5160. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35713211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expression and clinical significance of miR-132 in gastric cancer patients.Diagn Pathol. 2014 Mar 12;9:57. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-57. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24621117 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of P21-activated protein kinase 2 is an independent prognostic predictor for patients with gastric cancer.Diagn Pathol. 2014 Mar 12;9:55. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-55. Diagn Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24621074 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

