On-line protein capture on magnetic beads for ultrasensitive microfluidic immunoassays of cancer biomarkers
- PMID: 24144557
- PMCID: PMC3855669
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.09.054
On-line protein capture on magnetic beads for ultrasensitive microfluidic immunoassays of cancer biomarkers
Abstract
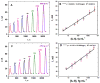
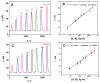
Accurate, sensitive, multiplexed detection of biomarker proteins holds significant promise for personalized cancer diagnostics. Here we describe the incorporation of a novel on-line chamber to capture cancer biomarker proteins on magnetic beads derivatized with 300,000 enzyme labels and 40,000 antibodies into a modular microfluidic immunoarray. Capture and detection chambers are produced from PDMS on machined molds and do not require lithography. Protein analytes are captured from serum or other biological samples in the stirred capture chamber on the beads held in place magnetically. The beads are subsequently washed free of sample components, and wash solutions sent to waste. Removal of the magnet and valve switching sends the magnetic bead-protein bioconjugates into a detection chamber where they are captured on 8 antibody-decorated gold nanoparticle-film sensors and detected amperometrically. Most steps in the immunoassay including protein capture, washing and measurement are incorporated into the device. In simultaneous assays, the microfluidic system gave ultralow detection limits of 5 fg mL(-1) for interleukin-6 (IL-6) and 7 fg mL(-1) for IL-8 in serum. Accuracy was demonstrated by measuring IL-6 and IL-8 in conditioned media from oral cancer cell lines and showing good correlations with standard ELISAs. The on-line capture chamber facilitates rapid, sensitive, repetitive protein separation and measurement in 30 min in a semi-automated system adaptable to multiplexed protein detection.
Keywords: Cancer biomarkers; Immunoarray; Magentic beads; Microfluidics; Protein detection.
© 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ultrasensitive detection of cancer biomarkers in the clinic by use of a nanostructured microfluidic array.Anal Chem. 2012 Jul 17;84(14):6249-55. doi: 10.1021/ac301392g. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22697359 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic electrochemical immunoarray for ultrasensitive detection of two cancer biomarker proteins in serum.Biosens Bioelectron. 2011 Jul 15;26(11):4477-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.05.005. Epub 2011 May 11. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011. PMID: 21632234 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive immunosensor for cancer biomarker proteins using gold nanoparticle film electrodes and multienzyme-particle amplification.ACS Nano. 2009 Mar 24;3(3):585-94. doi: 10.1021/nn800863w. ACS Nano. 2009. PMID: 19216571 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive protein detection: a case for microfluidic magnetic bead-based assays.Lab Chip. 2013 Dec 21;13(24):4711-39. doi: 10.1039/c3lc50477h. Lab Chip. 2013. PMID: 24145920 Review.
-
Nanomaterials for early detection of cancer biomarker with special emphasis on gold nanoparticles in immunoassays/sensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Jun 15;68:688-698. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.066. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25660660 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated multiplexed ECL Immunoarrays for cancer biomarker proteins.Anal Chem. 2015 Apr 21;87(8):4472-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00421. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25821929 Free PMC article.
-
Tunable Magneto-Plasmonic Nanosensor for Sensitive Detection of Foodborne Pathogens.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 7;13(1):109. doi: 10.3390/bios13010109. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671944 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging microfluidic devices for cancer cells/biomarkers manipulation and detection.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016 Oct;10(5):263-275. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2015.0060. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27676373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiplexed Electrochemical Cancer Diagnostics With Automated Microfluidics.Electroanalysis. 2019 Feb;31(2):208-211. doi: 10.1002/elan.201800632. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Electroanalysis. 2019. PMID: 32390709 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of disposable microfluidic chip design for automated and fast Immunoassays.Biomicrofluidics. 2017 Feb 22;11(1):014115. doi: 10.1063/1.4977198. eCollection 2017 Jan. Biomicrofluidics. 2017. PMID: 28344726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beveridge JS, Stephens JR, Williams ME. Anal Chem. 2011;4:251–273. - PubMed
-
- Chin CD, Laksanasopin T, Cheung YK, Steinmiller D, Linder V, Parsa H, Wang J, Moore H, Rouse R, Umviligihozo G, Karita E, Mwambarangwe L, Braunstein SL, van de Wijgert J, Sahabo R, Justman JE, El-Sadr W, Sia SK. Nature Med. 2011;17:1015–1019. - PubMed
-
- Chin CD, Linder V, Sia SK. Lab Chip. 2012;12:2118–2134. - PubMed
-
- Deckert F, Legay FO. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2000;23:403–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

