Regional variation in quality of prostate cancer care
- PMID: 24144685
- PMCID: PMC3980045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.10.066
Regional variation in quality of prostate cancer care
Abstract
Purpose: Despite the endorsement of several quality measures for prostate cancer by the National Quality Forum and the Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement, how consistently physicians adhere to these measures has not been examined. We evaluated regional variation in adherence to these quality measures to identify targets for future quality improvement.
Materials and methods: For this retrospective cohort study we used SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results)-Medicare data for 2001 to 2007 to identify 53,614 patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer. Patients were assigned to 661 regions (Hospital Service Areas). Hierarchical generalized linear models were used to examine reliability adjusted regional adherence to the endorsed quality measures.
Results: Adherence at the patient level was highly variable, ranging from 33% for treatment by a high volume provider to 76% for receipt of adjuvant androgen deprivation therapy while undergoing radiotherapy for high risk cancer. In addition, there was considerable regional variation in adherence to several measures, including pretreatment counseling by a urologist and radiation oncologist (range 9% to 89%, p <0.001), avoiding overuse of bone scans in low risk cancer (range 16% to 96%, p <0.001), treatment by a high volume provider (range 1% to 90%, p <0.001) and followup with radiation oncologists (range 14% to 86%, p <0.001).
Conclusions: We found low adherence rates for most established prostate cancer quality of care measures. Within most measures regional variation in adherence was pronounced. Measures with low adherence and a large amount of regional variation may be important low hanging targets for quality improvement.
Keywords: health services research; prostatic neoplasms; quality improvement; quality of health care; small-area analysis.
Copyright © 2014 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
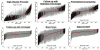
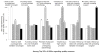
Comment in
-
Editorial comment.J Urol. 2014 Apr;191(4):962-3. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.10.149. Epub 2013 Dec 25. J Urol. 2014. PMID: 24373693 No abstract available.
References
-
- Spencer BA, Steinberg M, Malin J, et al. Quality-of-care indicators for early-stage prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1928–1936. - PubMed
-
- Thompson IM, Clauser S. [accessed September 13, 2011.];Prostate Cancer Physician Performance Measurement Set. 2007 Available at: http://www.ama-assn.org/apps/listserv/x-check/qmeasure.cgi?submit=PCPI.
-
- [accessed January 26, 2013.];National Quality Forum (NQF): NQF-endorsed standards. 2012 Available at: www.qualityforum.org/QPS/QPSTool.aspx?Exact=false&Keyword=prostatecancer.
-
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. [accessed July 5, 2012.];Physician Quality Reporting System: 2010 Reporting Experience Including Trends (2007–2011) 2012 Available at: http://www.facs.org/ahp/pqri/2013/2010experience-report.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

