Seedling Lethal1, a pentatricopeptide repeat protein lacking an E/E+ or DYW domain in Arabidopsis, is involved in plastid gene expression and early chloroplast development
- PMID: 24144791
- PMCID: PMC3850184
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.227199
Seedling Lethal1, a pentatricopeptide repeat protein lacking an E/E+ or DYW domain in Arabidopsis, is involved in plastid gene expression and early chloroplast development
Abstract
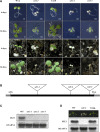
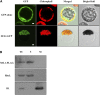
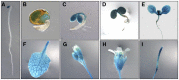
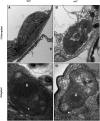
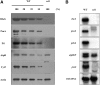
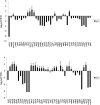
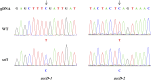
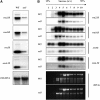
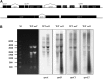
Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis and the biosynthesis of essential metabolites, including amino acids, fatty acids, and secondary metabolites. It is known that many seedling-lethal mutants are impaired in chloroplast function or development, indicating the development of functional chloroplast is essential for plant growth and development. Here, we isolated a novel transfer DNA insertion mutant, dubbed sel1 (for seedling lethal1), that exhibited a pigment-defective and seedling-lethal phenotype with a disrupted pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) gene. Sequence analysis revealed that SEL1 is a member of the PLS subgroup, which is lacking known E/E(+) or DYW domains at the C terminus, in the PLS subfamily of the PPR protein family containing a putative N-terminal transit peptide and 14 putative PPR or PPR-like motifs. Confocal microscopic analysis showed that the SEL1-green fluorescent protein fusion protein is localized in chloroplasts. Transmission electron microscopic analysis revealed that the sel1 mutant is impaired in the etioplast, as well as in chloroplast development. In sel1 mutants, plastid-encoded proteins involved in photosynthesis were rarely detected due to the lack of the corresponding transcripts. Furthermore, transcript profiles of plastid genes revealed that, in sel1 mutants, the transcript levels of plastid-encoded RNA polymerase-dependent genes were greatly reduced, but those of nuclear-encoded RNA polymerase-dependent genes were increased or not changed. Additionally, the RNA editing of two editing sites of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase beta subunit gene transcripts in the sel1 mutant was compromised, though it is not directly connected with the sel1 mutant phenotype. Our results demonstrate that SEL1 is involved in the regulation of plastid gene expression required for normal chloroplast development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A point mutation in the pentatricopeptide repeat motif of the AtECB2 protein causes delayed chloroplast development.J Integr Plant Biol. 2011 Apr;53(4):258-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2011.01030.x. Epub 2011 Mar 18. J Integr Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21294841
-
AtECB2, a pentatricopeptide repeat protein, is required for chloroplast transcript accD RNA editing and early chloroplast biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2009 Sep;59(6):1011-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03930.x. Epub 2009 May 28. Plant J. 2009. PMID: 19500301
-
The Arabidopsis gene YS1 encoding a DYW protein is required for editing of rpoB transcripts and the rapid development of chloroplasts during early growth.Plant J. 2009 Apr;58(1):82-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03766.x. Epub 2008 Dec 29. Plant J. 2009. PMID: 19054358
-
Mechanistic insight into pentatricopeptide repeat proteins as sequence-specific RNA-binding proteins for organellar RNAs in plants.Plant Cell Physiol. 2012 Jul;53(7):1171-9. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs069. Epub 2012 May 9. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22576772 Review.
-
Unveiling the functions of plastid ribosomal proteins in plant development and abiotic stress tolerance.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022 Oct 15;189:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.07.029. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36041366 Review.
Cited by
-
A PPR Protein ACM1 Is Involved in Chloroplast Gene Expression and Early Plastid Development in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 3;22(5):2512. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052512. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802303 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of conserved DUF177A protein in plastid 23S rRNA accumulation and plant embryogenesis.J Exp Bot. 2016 Oct;67(18):5447-5460. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw311. Epub 2016 Aug 29. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27574185 Free PMC article.
-
WSL6 encoding an Era-type GTP-binding protein is essential for chloroplast development in rice.Plant Mol Biol. 2019 Aug;100(6):635-645. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00885-z. Epub 2019 May 30. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31147815
-
Arabidopsis EMB1990 Encoding a Plastid-Targeted YlmG Protein Is Required for Chloroplast Biogenesis and Embryo Development.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Feb 16;9:181. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00181. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29503657 Free PMC article.
-
GUN1 and Plastid RNA Metabolism: Learning from Genetics.Cells. 2020 Oct 16;9(10):2307. doi: 10.3390/cells9102307. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33081381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arsova B, Hoja U, Wimmelbacher M, Greiner E, Ustün S, Melzer M, Petersen K, Lein W, Börnke F. (2010) Plastidial thioredoxin z interacts with two fructokinase-like proteins in a thiol-dependent manner: evidence for an essential role in chloroplast development in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell 22: 1498–1515 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aubourg S, Boudet N, Kreis M, Lecharny A. (2000) In Arabidopsis thaliana, 1% of the genome codes for a novel protein family unique to plants. Plant Mol Biol 42: 603–613 - PubMed
-
- Bang WY, Chen J, Jeong IS, Kim SW, Kim CW, Jung HS, Lee KH, Kweon HS, Yoko I, Shiina T, et al (2012) Functional characterization of ObgC in ribosome biogenesis during chloroplast development. Plant J 71:122–134 - PubMed
-
- Barkan A. (1998) Approaches to investigating nuclear genes that function in chloroplast biogenesis in land plants. Photosynthesis. Molecular Biology of Energy Capture 297: 38–57
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

