Extracellular transport of cell-size particles and tumor cells by dendritic cells in culture
- PMID: 24145002
- PMCID: PMC3953141
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.09.005
Extracellular transport of cell-size particles and tumor cells by dendritic cells in culture
Abstract
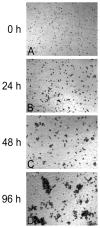
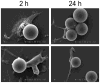
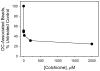
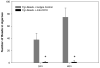
Many particulate materials of sizes approximating that of a cell disseminate after being introduced into the body. While some move about within phagocytic inflammatory cells, others appear to move about outside of, but in contact with, such cells. In this report, we provide unequivocal photomicroscopic evidence that cultured, mature, human dendritic cells can transport in extracellular fashion over significant distances both polymeric beads and tumor cells. At least in the case of polymeric beads, both fibrinogen and the β2-integrin subunit, CD18, appear to play important roles in the transport process. These discoveries may yield insight into a host of disease-related phenomena, including and especially tumor cell invasion and metastasis.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell-size particles; Chemotaxis; Dendritic cells; Directed migration; Extracellular transport; Inflammation; Metastasis; Tumor cells.
© 2013. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas AK, Lichtman AH. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. Saunders; Philadelphia: 2003a. Antigen Processing and Presentation to T Lymphocytes; pp. 88–90.
-
- Abbas AK, Lichtman AH. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. Saunders; Philadelphia: 2003b. Introduction to Immunology; pp. 24–26.
-
- Bachmann MF, et al. Chemokines: more than just road signs. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:159–64. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, et al. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:767–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

