Natural killer cell licensing in mice with inducible expression of MHC class I
- PMID: 24145414
- PMCID: PMC3831452
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1318255110
Natural killer cell licensing in mice with inducible expression of MHC class I
Abstract
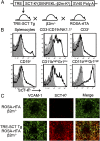
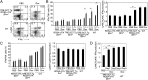
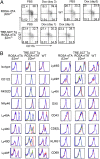
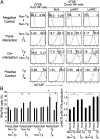
Mouse natural killer (NK) cells acquire effector function by an education process termed "licensing" mediated by inhibitory Ly49 receptors which recognize self-MHC class I. Ly49 receptors can bind to MHC class I on targets (in trans) and also to MHC class I on the NK-cell surface (in cis). Which of these interactions regulates NK-cell licensing is not yet clear. Moreover, there are no clear phenotypic differences between licensed and unlicensed NK cells, perhaps because of the previously limited ability to study NK cells with synchronized licensing. Here, we produced MHC class I-deficient mice with inducible MHC class I consisting of a single-chain trimer (SCT), ovalbumin peptide-β2 microgloblin-H2K(b) (SCT-K(b)). Only NK cells with a Ly49 receptor with specificity for SCT-K(b) were licensed after MHC class I induction. NK cells were localized consistently in red pulp of the spleen during induced NK-cell licensing, and there were no differences in maturation or activation markers on recently licensed NK cells. Although MHC class I-deficient NK cells were licensed in hosts following SCT-K(b) induction, NK cells were not licensed after induced SCT-K(b) expression on NK cells themselves in MHC class I-deficient hosts. Furthermore, hematopoietic cells with induced SCT-K(b) licensed NK cells more efficiently than stromal cells. These data indicate that trans interaction with MHC class I on hematopoietic cells regulates NK-cell licensing, which is not associated with other obvious phenotypic changes.
Keywords: immunity; lymphocytes; tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:225–274. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama WM. Natural killer cells. In: Paul WE, editor. Fundamental Immunology. 7th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013. pp. 395–431.
-
- Karlhofer FM, Ribaudo RK, Yokoyama WM. MHC class I alloantigen specificity of Ly-49+ IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Nature. 1992;358(6381):66–70. - PubMed
-
- Ljunggren HG, Kärre K. In search of the ‘missing self’: MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1990;11(7):237–244. - PubMed
-
- Liao NS, Bix M, Zijlstra M, Jaenisch R, Raulet D. MHC class I deficiency: Susceptibility to natural killer (NK) cells and impaired NK activity. Science. 1991;253(5016):199–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

