Structural basis for substrate specificity in the Escherichia coli maltose transport system
- PMID: 24145421
- PMCID: PMC3831462
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1311407110
Structural basis for substrate specificity in the Escherichia coli maltose transport system
Abstract
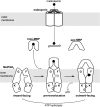
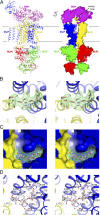
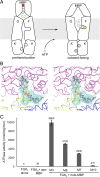
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are molecular pumps that harness the chemical energy of ATP hydrolysis to translocate solutes across the membrane. The substrates transported by different ABC transporters are diverse, ranging from small ions to large proteins. Although crystal structures of several ABC transporters are available, a structural basis for substrate recognition is still lacking. For the Escherichia coli maltose transport system, the selectivity of sugar binding to maltose-binding protein (MBP), the periplasmic binding protein, does not fully account for the selectivity of sugar transport. To obtain a molecular understanding of this observation, we determined the crystal structures of the transporter complex MBP-MalFGK2 bound with large malto-oligosaccharide in two different conformational states. In the pretranslocation structure, we found that the transmembrane subunit MalG forms two hydrogen bonds with malto-oligosaccharide at the reducing end. In the outward-facing conformation, the transmembrane subunit MalF binds three glucosyl units from the nonreducing end of the sugar. These structural features explain why modified malto-oligosaccharides are not transported by MalFGK2 despite their high binding affinity to MBP. They also show that in the transport cycle, substrate is channeled from MBP into the transmembrane pathway with a polarity such that both MBP and MalFGK2 contribute to the overall substrate selectivity of the system.
Keywords: maltodextrin; membrane protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Maltose-binding protein effectively stabilizes the partially closed conformation of the ATP-binding cassette transporter MalFGK2.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017 Apr 5;19(14):9366-9373. doi: 10.1039/c6cp07943a. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 28267156
-
Full engagement of liganded maltose-binding protein stabilizes a semi-open ATP-binding cassette dimer in the maltose transporter.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Dec;98(5):878-94. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13165. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26268698 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the maltose transporter in a pretranslocation intermediate state.Science. 2011 Jun 3;332(6034):1202-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1200767. Epub 2011 May 12. Science. 2011. PMID: 21566157
-
An integrated transport mechanism of the maltose ABC importer.Res Microbiol. 2019 Nov-Dec;170(8):321-337. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2019.09.004. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Res Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31560984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maltose transport system of Escherichia coli: an ABC-type transporter.FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):55-8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00315-7. FEBS Lett. 1994. PMID: 8206159 Review.
Cited by
-
The interplay between effector binding and allostery in an engineered protein switch.Protein Sci. 2016 Sep;25(9):1605-16. doi: 10.1002/pro.2962. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27272021 Free PMC article.
-
Novel functional insights into a modified sugar-binding protein from Synechococcus MITS9220.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 21;12(1):4805. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08459-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35314715 Free PMC article.
-
Maltotriose-based probes for fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging of bacterial infections.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 6;11(1):1250. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14985-8. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32144257 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular details of a starch utilization pathway in the human gut symbiont Eubacterium rectale.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Jan;95(2):209-30. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12859. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25388295 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Transcriptome Analysis of Mature Biofilm and Planktonic Cells of Salmonella Enteritidis Exposure to Acid Stress.Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 26;8:1861. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01861. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29018430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holland IB, Cole SPC, Kuchler K, editors. ABC Proteins: From Bacteria to Man. New York: Academic Press; 2003.
-
- Li Y, et al. The structure and functions of P-glycoprotein. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(8):786–800. - PubMed
-
- Dawson RJ, Hollenstein K, Locher KP. Uptake or extrusion: Crystal structures of full ABC transporters suggest a common mechanism. Mol Microbiol. 2007;65(2):250–257. - PubMed
-
- Ferenci T. The recognition of maltodextrins by Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(2):631–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

