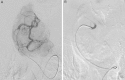
The calcium-phosphate balance, modulation of thyroid autoimmune processes and other adverse effects connected with thyroid arterial embolization
- PMID: 24146411
- PMCID: PMC4040001
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-013-0072-2
The calcium-phosphate balance, modulation of thyroid autoimmune processes and other adverse effects connected with thyroid arterial embolization
Abstract
In search of new treatment options for thyroid diseases, when conventional procedures are ineffective, contraindicated or associated with serious side effects, safety of thyroid arteries embolization in the treatment of particular thyroid diseases was evaluated. The study included eight subjects with retrosternal toxic goiter, six patients affected by Graves' disease, five cases of retrosternal non-toxic goiter, two subjects with post-amiodarone hyperthyroidism, and one patient with severe thyroid-related orbitopathy, who underwent selective embolization of thyroid arteries. The study assessed and compared calcium-phosphate balance, modulation of thyroid autoimmunity and the presence of different side effects in patients who underwent the procedure. In addition, the serum concentrations of thyroid hormones, anti-thyroid autoantibodies and thyroid volume have been measured. Five of all enrolled subjects (22.7 %) experienced transient, not clinically relevant hypocalcaemia with no need for calcium supplementation. There were no significant changes in serum calcium levels in patients after embolization of both inferior thyroid arteries. The transient side effects associated with the treatment were neck pain and a slight increase in body temperature. Noted high concentration of free thyroid hormones immediately after the procedure was not accompanied by worsening of symptoms or signs of thyrotoxicosis. In patients with Graves' disease, a significant decrease in thyrotropin receptor antibodies level was observed. Thyroid arterial embolization does not disturb permanently calcium-phosphate balance, modulates positively thyroid autoimmune processes and is associated with no serious post-procedure side effects. Hence, it may be considered as a safe and effective treatment modality for selected thyroid disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Arterial embolization: a novel approach to thyroid ablative therapy for Graves' disease.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Aug;87(8):3583-9. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.8.8723. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12161479 Clinical Trial.
-
Graves' disease treated with thyroid arterial embolization.Clin Invest Med. 2009 Apr 1;32(2):E158-65. doi: 10.25011/cim.v32i2.6034. Clin Invest Med. 2009. PMID: 19331805
-
Thyroid arterial embolization to treat Graves' disease.Acta Radiol. 2007 Mar;48(2):186-92. doi: 10.1080/02841850601128967. Acta Radiol. 2007. PMID: 17354140
-
Thyroid autoimmunity and thyroid autonomy.Acta Med Austriaca. 1990;17 Suppl 1:90-2. Acta Med Austriaca. 1990. PMID: 2202187 Review.
-
Diagnosis and classification of Graves' disease.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Apr-May;13(4-5):398-402. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.013. Epub 2014 Jan 12. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 24424182 Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid Artery Embolization for Tracheostomy Site Bleeding: A Report of Three Cases.J Korean Soc Radiol. 2024 Sep;85(5):976-980. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2023.0160. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39416318 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid arterial embolization in a patient with congenital heart disease and refractory amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis.Eur Thyroid J. 2022 Jan 1;11(1):e210007. doi: 10.1530/ETJ-21-0007. Eur Thyroid J. 2022. PMID: 34981740 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial embolization outperforms radiofrequency ablation for thyroid goiters exceeding 100 mL: a study on efficacy and safety.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jul 14. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11791-y. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40658200
References
-
- Bjoro T, Holmen J, Kruger O, Midthjell K, Hunstad K, Schreiner T, Sandnes L, Brochmann H. Prevalence of thyroid disease, thyroid dysfunction and thyroid peroxidase antibodies in a large, unselected population. The Health Study of Nord-Trondelag (HUNT) Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2000;143(5):639–647. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1430639. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xiao H, Zhuang W, Wang S, Yu B, Chen G, Zhou M, Wong NC. Arterial embolization: a novel approach to thyroid ablative therapy for Graves’ disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002;87(8):3583–3589. - PubMed
-
- Lee CH, Liang RH. Antithyroid drug-induced agranulocytosis. Hong Kong Med. J. 1999;5(4):394–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical