Determination of antimicrobial effect, antioxidant activity and phenolic contents of desert truffle in Turkey
- PMID: 24146501
- PMCID: PMC3794391
Determination of antimicrobial effect, antioxidant activity and phenolic contents of desert truffle in Turkey
Abstract
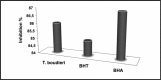
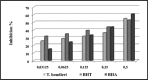
Terfezia boudieri Chatin (Scop.) Pers., is a famous macrofungus in the world as well as in Turkey for its pleasant aroma and flavour. People believe that this mushroom has some medicinal properties. Therefore, it is consumed as food and for medicinal purposes. Chloroform, acetone and methanol extracts of T. boudieri were tested to reveal its antimicrobial activity against four Gram-positive and five Gram-negative bacteria, and one yeast using a micro dilution method. In this study, the highest minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value was observed with the acetone extract (MIC, 4.8 µg/mL) against Candida albicans. Maximum antimicrobial effect was also determined with the acetone extract (MIC, 39-78 µg/mL). The scavenging effect of T. boudieri on 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals was measured as 0.031 mg/mL at 5 mg/mL concentration, and its reducing power was 0.214 mg/mL at 0.4 mg/mL. In addition, the phenolic contents were determined as follows: the catechin was 20 mg/g, the ferulic acid was 15 mg/g, the p-coumaric acid was 10 mg/g, and the cinnamic acid was 6 mg/g. The results showed that T. boudieri has antimicrobial activity on the gram negative and positive bacteria as well as yeast, and it also has a high antioxidant capacity. Therefore, T. boudieri can be recommended as an important natural food source.
Keywords: Gram positive and negative bacteria; Terfezia boudieri; medical mushroom; scavenging effect.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial activities of some mushrooms in Turkey.Pharm Biol. 2013 Jun;51(6):707-11. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2013.764327. Pharm Biol. 2013. PMID: 23675836
-
Biological activity and fatty acid composition of Caesar's mushroom.Pharm Biol. 2013 Jul;51(7):863-71. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2013.768272. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Pharm Biol. 2013. PMID: 23527891
-
Some biological activities of Lactarius vellereus (Fr.) Fr. in Turkey.Pak J Biol Sci. 2013 Nov 1;16(21):1279-86. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2013.1279.1286. Pak J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24511735
-
A comparative study on phenolic components and biological activity of some Senecio species in Turkey.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014 Nov;66(11):1631-40. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12288. Epub 2014 Jun 19. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24945637
-
Natural Compounds with Oxepinochromene Scaffold. Structure, Source, Biological Activity and Synthesis.Chem Biodivers. 2022 Nov;19(11):e202200507. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202200507. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Chem Biodivers. 2022. PMID: 36226917 Review.
Cited by
-
Potentials of truffles in nutritional and medicinal applications: a review.Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 17;7:9. doi: 10.1186/s40694-020-00097-x. eCollection 2020. Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32566240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial efficacy of extracts of Saudi Arabian desert Terfezia claveryi truffles.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Nov;29(11):103462. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103462. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36267911 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Partial Structure and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Two Species of Chinese Truffles.Molecules. 2020 Sep 22;25(18):4345. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184345. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32971949 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental conditions influence the biochemical properties of the fruiting bodies of Tuber magnatum Pico.Sci Rep. 2018 May 8;8(1):7243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25520-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29740145 Free PMC article.
-
Tour of Truffles: Aromas, Aphrodisiacs, Adaptogens, and More.Mycobiology. 2021 Jul 1;49(3):201-212. doi: 10.1080/12298093.2021.1936766. eCollection 2021. Mycobiology. 2021. PMID: 34290545 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Astier J. Truffes blanches et noires. Marseille: Louis-Jean, Gap; 1998. pp. 48–49.
-
- Cheung LM, Cheung Peter C K, Vincent EC. Antioxidant activity and total phenolics of edible mushroom extracts. Food Chem. 2003;81:249–255.
-
- Craig WA. Pharmocokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters: rationale for antibacterial dosing of mice and men. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Devienne KF, Raddi MSG. Screening for antimicrobial activity of natural products using a microplate photometer. Braz J Microbiol. 2002;33:166–168.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
