Impaired decisional impulsivity in pathological videogamers
- PMID: 24146789
- PMCID: PMC3797823
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075914
Impaired decisional impulsivity in pathological videogamers
Abstract
Background: Pathological gaming is an emerging and poorly understood problem. Impulsivity is commonly impaired in disorders of behavioural and substance addiction, hence we sought to systematically investigate the different subtypes of decisional and motor impulsivity in a well-defined pathological gaming cohort.
Methods: Fifty-two pathological gaming subjects and age-, gender- and IQ-matched healthy volunteers were tested on decisional impulsivity (Information Sampling Task testing reflection impulsivity and delay discounting questionnaire testing impulsive choice), and motor impulsivity (Stop Signal Task testing motor response inhibition, and the premature responding task). We used stringent diagnostic criteria highlighting functional impairment.
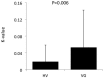
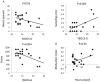
Results: In the Information Sampling Task, pathological gaming participants sampled less evidence prior to making a decision and scored fewer points compared with healthy volunteers. Gaming severity was also negatively correlated with evidence gathered and positively correlated with sampling error and points acquired. In the delay discounting task, pathological gamers made more impulsive choices, preferring smaller immediate over larger delayed rewards. Pathological gamers made more premature responses related to comorbid nicotine use. Greater number of hours played also correlated with a Motivational Index. Greater frequency of role playing games was associated with impaired motor response inhibition and strategy games with faster Go reaction time.
Conclusions: We show that pathological gaming is associated with impaired decisional impulsivity with negative consequences in task performance. Decisional impulsivity may be a potential target in therapeutic management.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impulsivity and related neuropsychological features in regular and addictive first person shooter gaming.Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2014 Mar;17(3):147-52. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2013.0024. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2014. PMID: 23971428
-
Established risk factors for addiction fail to discriminate between healthy gamers and gamers endorsing DSM-5 Internet gaming disorder.J Behav Addict. 2017 Dec 1;6(4):516-524. doi: 10.1556/2006.6.2017.074. Epub 2017 Nov 13. J Behav Addict. 2017. PMID: 29130328 Free PMC article.
-
Is experience in multi-genre video game playing accompanied by impulsivity?Acta Psychol (Amst). 2018 Oct;190:78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2018.07.006. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2018. PMID: 30031355
-
Inhibition and impulsivity: behavioral and neural basis of response control.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Sep;108:44-79. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.005. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23856628 Review.
-
Assaying dissociable elements of behavioural inhibition and impulsivity: translational utility of animal models.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;11(5):534-9. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2011.06.006. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21763200 Review.
Cited by
-
Impulsivity traits and addiction-related behaviors in youth.J Behav Addict. 2018 Jun 1;7(2):317-330. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.22. Epub 2018 Apr 12. J Behav Addict. 2018. PMID: 29642723 Free PMC article.
-
Profiles of Impulsivity in Problematic Internet Users and Cigarette Smokers.Front Psychol. 2019 Apr 4;10:772. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00772. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31019482 Free PMC article.
-
Can Worried Parents Predict Effects of Video Games on Their Children? A Case-Control Study of Cognitive Abilities, Addiction Indicators and Wellbeing.Front Psychol. 2021 Jan 15;11:586699. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.586699. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 33536966 Free PMC article.
-
Disordered gambling: the evolving concept of behavioral addiction.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014 Oct;1327(1):46-61. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12558. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014. PMID: 25336388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropsychological Deficits in Disordered Screen Use Behaviours: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Neuropsychol Rev. 2024 Sep;34(3):791-822. doi: 10.1007/s11065-023-09612-4. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Neuropsychol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37695451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gentile DA, Choo H, Liau A, Sim T, Li D, et al. (2011) Pathological video game use among youths: a two-year longitudinal study. Pediatrics 127: e319–329. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson CJ, Coulson M, Barnett J (2011) A meta-analysis of pathological gaming prevalence and comorbidity with mental health, academic and social problems. J Psychiatr Res 45: 1573–1578. - PubMed
-
- APA APA announces draft diagnostic criteria for DSM-5: new proposed changes posted for leading manual of mental disorders.
-
- Gentile D (2009) Pathological video-game use among youth ages 8 to 18: a national study. Psychol Sci 20: 594–602. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths MD, Hunt N (1998) Dependence on computer games by adolescents. Psychol Rep 82: 475–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

