Chinese herbal medicine for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: an updated meta-analysis of 10 high-quality randomized controlled studies
- PMID: 24146822
- PMCID: PMC3797714
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076113
Chinese herbal medicine for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: an updated meta-analysis of 10 high-quality randomized controlled studies
Abstract
Background: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is very common in people with diabetes. Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) therapy has been developed for DPN empirically over the years. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to assess the efficacy and safety of CHMs for patients suffering from DPN.
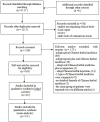
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis of randomized-controlled clinical trials (RCTs) evaluating the efficacy and safety of CHM on DPN. Six databases were searched up to November 2012. The primary outcome measures were the absolute values or changing of motor or sensory nerve conduction velocity (NCV), and the secondary outcome measurements were clinical symptoms improvements and adverse events. The methodological quality was assessed by Jadad scale and the twelve criteria recommended by the Cochrane Back Review Group.
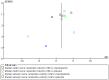
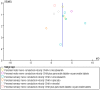
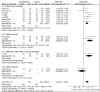
Results: One hundred and sixty-three studies claimed RCTs. Ten studies with 653 individuals were further identified based on the Jadad score ≥ 3. These 10 studies were all of high methodological quality with a low risk of bias. Meta-analysis showed the effects of NCV favoring CHMs when compared with western conventional medicines (WCM) (P<0.05 or P<0.01). There is a significant difference in the total efficacy rate between the two groups (P<0.001). Adverse effects were reported in all of the ten included studies, and well tolerated in all patients with DPN.
Conclusion: Despite of the apparently positive findings and low risk of bias, it is premature to conclude the efficacy of CHMs for the treatment of DPN because of the high clinical heterogeneity and small sample sizes of the included studies. However, CHM therapy was safe for DPN. Further standardized preparation, large sample-size and rigorously designed RCTs are required.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Are herbal medicines alone or in combination for diabetic peripheral neuropathy more effective than methylcobalamin alone? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2022 Nov;49:101657. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2022.101657. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36007447
-
Zusanli (ST36) Acupoint Injection for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Altern Complement Med. 2018 Dec;24(12):1138-1149. doi: 10.1089/acm.2018.0053. Epub 2018 Sep 26. J Altern Complement Med. 2018. PMID: 30431314 Free PMC article.
-
[Systematic review and Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Shuxuetong Injection in treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jun;47(11):3088-3094. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220303.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35718533 Chinese.
-
Moxibustion for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis following PRISMA guidelines.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 25;99(39):e22286. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022286. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32991431 Free PMC article.
-
Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Protocol for a systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Aug;98(31):e16696. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016696. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31374060 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dilemmas in Elderly Diabetes and Clinical Practice Involving Traditional Chinese Medicine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;17(7):953. doi: 10.3390/ph17070953. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term efficacy and safety of Huangqi ()-based Traditional Chinese Medicine in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Apr;44(2):229-242. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2024.02.004. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38504529 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine attenuates hospitalization and mortality risks in diabetic patients with carcinoma in situ in Taiwan.Integr Med Res. 2022 Jun;11(2):100831. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2021.100831. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Integr Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35059290 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive Effects of the Chinese Herbal Medicine Prescription Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities on Sciatic Neuropathy in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:9138328. doi: 10.1155/2016/9138328. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27057201 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine TangBi Formula treatment of patients with type 2 diabetic distal symmetric polyneuropathy disease: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2017 Dec 29;18(1):631. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2345-1. Trials. 2017. PMID: 29284520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, Bril V, Feldman EL, et al... (2005) American Diabetes Association. Diabetic Neuropathies A statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 28: 956–962. PubMed: 15793206. - PubMed
-
- Perkins BA, Greene DA, Bril V (2001) Glycemic control is related to the morphological severity of diabetic peripheral sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 24: 748–752. PubMed: 11315842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

