Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-1) Ec/Mechano Growth factor--a splice variant of IGF-1 within the growth plate
- PMID: 24146828
- PMCID: PMC3795771
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076133
Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-1) Ec/Mechano Growth factor--a splice variant of IGF-1 within the growth plate
Abstract
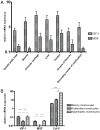
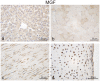
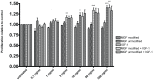
Human insulin-like growth factor 1 Ec (IGF-1Ec), also called mechano growth factor (MGF), is a splice variant of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which has been shown in vitro as well as in vivo to induce growth and hypertrophy in mechanically stimulated or damaged muscle. Growth, hypertrophy and responses to mechanical stimulation are important reactions of cartilaginous tissues, especially those in growth plates. Therefore, we wanted to ascertain if MGF is expressed in growth plate cartilage and if it influences proliferation of chondrocytes, as it does in musculoskeletal tissues. MGF expression was analyzed in growth plate and control tissue samples from piglets aged 3 to 6 weeks. Furthermore, growth plate chondrocyte cell culture was used to evaluate the effects of the MGF peptide on proliferation. We showed that MGF is expressed in considerable amounts in the tissues evaluated. We found the MGF peptide to be primarily located in the cytoplasm, and in some instances, it was also found in the nucleus of the cells. Addition of MGF peptides was not associated with growth plate chondrocyte proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mechano-growth factor protects against mechanical overload induced damage and promotes migration of growth plate chondrocytes through RhoA/YAP pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2018 May 15;366(2):81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.02.021. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29470961
-
Different roles of the IGF-I Ec peptide (MGF) and mature IGF-I in myoblast proliferation and differentiation.FEBS Lett. 2002 Jul 3;522(1-3):156-60. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)02918-6. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12095637
-
Increased IGF-IEc expression and mechano-growth factor production in intestinal muscle of fibrostenotic Crohn's disease and smooth muscle hypertrophy.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Dec 1;309(11):G888-99. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00414.2014. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26428636 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of IGF-I gene splicing and MGF expression associated with muscle wasting.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;38(3):481-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.10.001. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16463438 Review.
-
IGF-IEc expression, regulation and biological function in different tissues.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2010 Aug;20(4):275-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2010.03.005. Epub 2010 May 21. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2010. PMID: 20494600 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-PEc: Development of a novel monoclonal antibody against prostate cancer.Br J Cancer. 2024 Aug;131(3):551-564. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02713-8. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38902531 Free PMC article.
-
IGF1 potentiates BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells through the enhancement of BMP/Smad signaling.BMB Rep. 2016 Feb;49(2):122-7. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.2.228. BMB Rep. 2016. PMID: 26645636 Free PMC article.
-
IGF-IEc expression is increased in secondary compared to primary foci in neuroendocrine neoplasms.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 8;8(45):79003-79011. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20743. eCollection 2017 Oct 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29108282 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-497-5p inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Oct;7(10):e00860. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.860. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. Retraction in: Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023 Jan;11(1):e2114. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2114. PMID: 31441605 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Flow perfusion effects on three-dimensional culture and drug sensitivity of Ewing sarcoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 18;112(33):10304-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506684112. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26240353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Green H, Morikawa M, Nixon T (1985) A dual effector theory of growth-hormone action. Differentiation 29: 195–198. - PubMed
-
- Isaksson OG, Lindahl A, Nilsson A, Isgaard J (1987) Mechanism of the stimulatory effect of growth hormone on longitudinal bone growth. Endocr Rev 8: 426–438. - PubMed
-
- Le Roith D, Bondy C, Yakar S, Liu JL, Butler A (2001) The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001. Endocr Rev 22: 53–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

