Modeling the neurovascular niche: unbiased transcriptome analysis of the murine subventricular zone in response to hypoxic insult
- PMID: 24146847
- PMCID: PMC3795763
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076265
Modeling the neurovascular niche: unbiased transcriptome analysis of the murine subventricular zone in response to hypoxic insult
Abstract
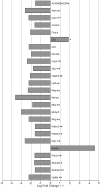
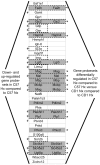
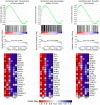
Premature infants often experience chronic hypoxia, resulting in cognitive & motor neurodevelopmental handicaps. These sometimes devastating handicaps are thought to be caused by compromised neural precursor cell (NPC) repair/recovery resulting in variable central nervous system (CNS) repair/recovery. We have identified differential responses of two mouse strains (C57BL/6 & CD1) to chronic hypoxia that span the range of responsiveness noted in the premature human population. We previously correlated several CNS tissue and cellular behaviors with the different behavioral parameters manifested by these two strains. In this report, we use unbiased array technology to interrogate the transcriptome of the subventricular zone (SVZ) in these strains. Our results illustrate differences in mRNA expression in the SVZ of both C57BL/6 and CD1 mice following hypoxia as well as differences between C57BL/6 and CD1 SVZ under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Differences in expression were found in gene sets associated with Sox10-mediated neural functions that explain, in part, the differential cognitive and motor responsiveness to hypoxic insult. This may shed additional light on our understanding of the variable responses noted in the human premature infant population and facilitate early intervention approaches. Further interrogation of the differentially expressed gene sets will provide a more complete understanding of the differential responses to, and recovery from, hypoxic insult allowing for more informed modeling of the ranges of disease severity observed in the very premature human population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
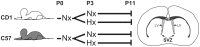
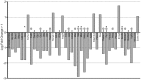
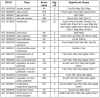
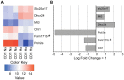
Similar articles
-
Modulation of Sox10, HIF-1α, Survivin, and YAP by Minocycline in the Treatment of Neurodevelopmental Handicaps following Hypoxic Insult.Am J Pathol. 2015 Sep;185(9):2364-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.05.016. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26209807 Free PMC article.
-
Strain differences in behavioral and cellular responses to perinatal hypoxia and relationships to neural stem cell survival and self-renewal: Modeling the neurovascular niche.Am J Pathol. 2009 Nov;175(5):2133-46. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090354. Epub 2009 Oct 8. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19815710 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the neurovascular niche: murine strain differences mimic the range of responses to chronic hypoxia in the premature newborn.J Neurosci Res. 2008 May 1;86(6):1227-42. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21597. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18092360 Free PMC article.
-
Gene profiles within the adult subventricular zone niche: proliferation, differentiation and migration of neural progenitor cells in the ischemic brain.Curr Mol Med. 2007 Aug;7(5):459-62. doi: 10.2174/156652407781387136. Curr Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17691960 Review.
-
Modeling the neurovascular niche: implications for recovery from CNS injury.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;60 Suppl 4:95-104. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20083857 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of different strain backgrounds in bacterial endotoxin-mediated sensitization to neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Neuroscience. 2015 Dec 17;311:292-307. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.10.035. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26515746 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Sox10, HIF-1α, Survivin, and YAP by Minocycline in the Treatment of Neurodevelopmental Handicaps following Hypoxic Insult.Am J Pathol. 2015 Sep;185(9):2364-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.05.016. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26209807 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of gene expression changes in human neural stem cells and endothelial cells modeling a neurovascular microenvironment.Brain Res Bull. 2020 May;158:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.02.008. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 32092433 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline mitigates the effect of neonatal hypoxic insult on human brain organoids.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Apr 11;10(4):325. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1553-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30975982 Free PMC article.
-
The role of endothelial HIF-1 αin the response to sublethal hypoxia in C57BL/6 mouse pups.Lab Invest. 2017 Apr;97(4):356-369. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.154. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Lab Invest. 2017. PMID: 28092362
References
-
- Wilson-Costello D, Friedman H, Minich N, Fanaroff AA, Hack M (2005) Improved survival rates with increased neurodevelopmental disability for extremely low birth weight infants in the 1990s. Pediatrics 115: 997–1003. - PubMed
-
- Tyson JE, Saigal S (2005) Outcomes for extremely low-birth-weight infants: disappointing news. JAMA 294: 371–373. - PubMed
-
- Saigal S, Stoskopf B, Streiner D, Boyle M, Pinelli J, et al. (2006) Transition of extremely low-birth-weight infants from adolescence to young adulthood: comparison with normal birth-weight controls. JAMA 295: 667–675. - PubMed
-
- Hack M, Flannery DJ, Schluchter M, Cartar L, Borawski E, et al. (2002) Outcomes in young adulthood for very-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med 346: 149–157. - PubMed
-
- Saigal S, Doyle LW (2008) An overview of mortality and sequelae of preterm birth from infancy to adulthood. Lancet 371: 261–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

