Anti-inflammatory effect of targeted delivery of SOD to endothelium: mechanism, synergism with NO donors and protective effects in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 24146950
- PMCID: PMC3795626
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077002
Anti-inflammatory effect of targeted delivery of SOD to endothelium: mechanism, synergism with NO donors and protective effects in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
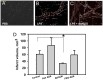
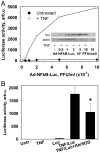
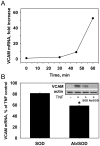
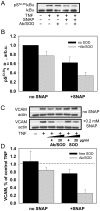
Pro-inflammatory activation of vascular endothelium is implicated in pathogenesis of severe conditions including stroke, infarction and sepsis. We have recently reported that superoxide dismutase (SOD) conjugated with antibodies (Ab/SOD) that provide targeted delivery into endothelial endosomes mitigates inflammatory endothelial activation by cytokines and agonists of Toll-like receptors (TLR). The goal of this study was to appraise potential utility and define the mechanism of this effect. Ab/SOD, but not non-targeted SOD injected in mice alleviated endotoxin-induced leukocyte adhesion in the cerebral vasculature and protected brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transfection of endothelial cells with SOD, but not catalase inhibited NFκB signaling and expression of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 induced by both cytokines and TLR agonists. These results affirmed that Ab/SOD-quenched superoxide anion produced by endothelial cells in response to proinflammatory agents mediates NFκB activation. Furthermore, Ab/SOD potentiates anti-inflammatory effect of NO donors in endothelial cells in vitro, as well as in the endotoxin-challenged mice. These results demonstrate the central role of intracellular superoxide as a mediator of pro-inflammatory activation of endothelium and support the notion of utility of targeted interception of this signaling pathway for management of acute vascular inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Thomas SR, Witting PK, Drummond GR (2008) Redox control of endothelial function and dysfunction: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 10: 1713–1765. - PubMed
-
- Yeh LH, Kinsey AM, Chatterjee S, Alevriadou BR (2001) Lactosylceramide mediates shear-induced endothelial superoxide production and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression. J Vasc Res 38: 551–559. - PubMed
-
- Pober JS, Sessa WC (2007) Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 7: 803–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

