The tumor suppressor gene TUSC2 (FUS1) sensitizes NSCLC to the AKT inhibitor MK2206 in LKB1-dependent manner
- PMID: 24146957
- PMCID: PMC3798310
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077067
The tumor suppressor gene TUSC2 (FUS1) sensitizes NSCLC to the AKT inhibitor MK2206 in LKB1-dependent manner
Abstract
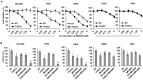
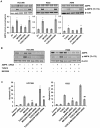
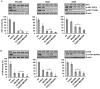
TUSC2-defective gene expression is detected in the majority of lung cancers and is associated with worse overall survival. We analyzed the effects of TUSC2 re-expression on tumor cell sensitivity to the AKT inhibitor, MK2206, and explored their mutual signaling connections, in vitro and in vivo. TUSC2 transient expression in three LKB1-defective non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines combined with MK2206 treatment resulted in increased repression of cell viability and colony formation, and increased apoptotic activity. In contrast, TUSC2 did not affect the response to MK2206 treatment for two LKB1-wild type NSCLC cell lines. In vivo, TUSC2 systemic delivery, by nanoparticle gene transfer, combined with MK2206 treatment markedly inhibited growth of tumors in a human LKB1-defective H322 lung cancer xenograft mouse model. Biochemical analysis showed that TUSC2 transient expression in LKB1-defective NSCLC cells significantly stimulated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and enzymatic activity. More importantly, AMPK gene knockdown abrogated TUSC2-MK2206 cooperation, as evidenced by reduced sensitivity to the combined treatment. Together, TUSC2 re-expression and MK2206 treatment was more effective in inhibiting the phosphorylation and kinase activities of AKT and mTOR proteins than either single agent alone. In conclusion, these findings support the hypothesis that TUSC2 expression status is a biological variable that potentiates MK2206 sensitivity in LKB1-defective NSCLC cells, and identifies the AMPK/AKT/mTOR signaling axis as an important regulator of this activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Combination treatment with MEK and AKT inhibitors is more effective than each drug alone in human non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 29;5(11):e14124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014124. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124782 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous Restoration of TUSC2 Expression Induces Responsiveness to Erlotinib in Wildtype Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Lung Cancer Cells through Context Specific Pathways Resulting in Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 8;10(6):e0123967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123967. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26053020 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol ether lipid analogues induce AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent death in LKB1-mutant non small cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2008 Jan 15;68(2):580-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3091. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18199555 Free PMC article.
-
LKB1/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(7):4033-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.7.4033. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23991948 Review.
-
LKB1/AMPK Pathway and Drug Response in Cancer: A Therapeutic Perspective.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 31;2019:8730816. doi: 10.1155/2019/8730816. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31781355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor suppressor candidate 2 (TUSC2, FUS-1) and human cancers.Discov Med. 2017 May;23(128):325-330. Discov Med. 2017. PMID: 28715648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TUSC2 immunogene enhances efficacy of chemo-immuno combination on KRAS/LKB1 mutant NSCLC in humanized mouse model.Commun Biol. 2022 Feb 24;5(1):167. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03103-7. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35210547 Free PMC article.
-
The TUSC2 Tumour Suppressor Inhibits the Malignant Phenotype of Human Thyroid Cancer Cells via SMAC/DIABLO Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 21;21(3):702. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030702. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31973107 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Suppressor Candidate 2 (TUSC2): Discovery, Functions, and Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 25;15(9):2455. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092455. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TUSC2 Immunogene Therapy Synergizes with Anti-PD-1 through Enhanced Proliferation and Infiltration of Natural Killer Cells in Syngeneic Kras-Mutant Mouse Lung Cancer Models.Cancer Immunol Res. 2018 Feb;6(2):163-177. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0273. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Cancer Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29339375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lerman MI, Minna JD (2000) The 630-kb lung cancer homozygous deletion region on human chromosome 3p21.3: identification and evaluation of the resident candidate tumor suppressor genes. The International Lung Cancer Chromosome 3p21.3 Tumor Suppressor Gene Consortium. Cancer Res 60(21): 6116–6133. - PubMed
-
- Li G, Kawashima H, Ji L, Ogose A, Ariizumi T, et al. (2011) Frequent absence of tumor suppressor FUS1 protein expression in human bone and soft tissue sarcomas. Anticancer Res 31(1): 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Gopalan B, Ito I, Branch CD, Stephens C, Roth JA, et al. (2004) Nanoparticle based systemic gene therapy for lung cancer: molecular mechanisms and strategies to suppress nanoparticle-mediated inflammatory response. Technol Cancer Res Treat 3(6): 647–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

