Toxicity and immunogenicity of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile and heat-stable toxoid fusion 3xSTa(A14Q)-LT(S63K/R192G/L211A) in a murine model
- PMID: 24146989
- PMCID: PMC3795625
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077386
Toxicity and immunogenicity of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-labile and heat-stable toxoid fusion 3xSTa(A14Q)-LT(S63K/R192G/L211A) in a murine model
Abstract
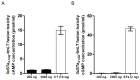
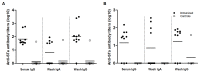
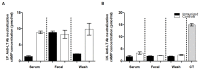
Diarrhea is the second leading cause of death to young children. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) are the most common bacteria causing diarrhea. Adhesins and enterotoxins are the virulence determinants in ETEC diarrhea. Adhesins mediate bacterial attachment and colonization, and enterotoxins including heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable type Ib toxin (STa) disrupt fluid homeostasis in host cells that leads to fluid hyper-secretion and diarrhea. Thus, adhesins and enterotoxins have been primarily targeted in ETEC vaccine development. A recent study reported toxoid fusions with STa toxoid (STa(P13F)) fused at the N- or C-terminus, or inside the A subunit of LT(R192G) elicited neutralizing antitoxin antibodies, and suggested application of toxoid fusions in ETEC vaccine development (Liu et al., Infect. Immun. 79:4002-4009, 2011). In this study, we generated a different STa toxoid (STa(A14Q)) and a triple-mutant LT toxoid (LT(S63K/R192G/L211A), tmLT), constructed a toxoid fusion (3xSTa(A14Q)-tmLT) that carried 3 copies of STa(A14Q) for further facilitation of anti-STa immunogenicity, and assessed antigen safety and immunogenicity in a murine model to explore its potential for ETEC vaccine development. Mice immunized with this fusion antigen showed no adverse effects, and developed antitoxin antibodies particularly through the IP route. Anti-LT antibodies were detected and were shown neutralizing against CT in vitro. Anti-STa antibodies were also detected in the immunized mice, and serum from the IP immunized mice neutralized STa toxin in vitro. Data from this study indicated that toxoid fusion 3xSTa(A14Q)-tmLT is safe and can induce neutralizing antitoxin antibodies, and provided helpful information for vaccine development against ETEC diarrhea.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


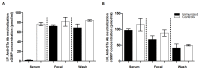
Similar articles
-
Neutralizing Anti-Heat-Stable Toxin (STa) Antibodies Derived from Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Toxoid Fusions with STa Proteins Containing N12S, L9A/N12S, or N12S/A14T Mutations Show Little Cross-Reactivity with Guanylin or Uroguanylin.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jan 2;84(2):e01737-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01737-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29079628 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-labile- and heat-stable-toxoid fusions (LTR₁₉₂G-STaP₁₃F) of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli elicit neutralizing antitoxin antibodies.Infect Immun. 2011 Oct;79(10):4002-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00165-11. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21788385 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Adhesin-Toxoid Multiepitope Fusion Antigen CFA/I/II/IV-3xSTaN12S-mnLTG192G/L211A-Derived Antibodies Inhibit Adherence of Seven Adhesins, Neutralize Enterotoxicity of LT and STa Toxins, and Protect Piglets against Diarrhea.Infect Immun. 2018 Feb 20;86(3):e00550-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00550-17. Print 2018 Mar. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29263112 Free PMC article.
-
Current Progress in Developing Subunit Vaccines against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Associated Diarrhea.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Sep;22(9):983-91. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00224-15. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26135975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine based on the heat-stable toxin.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(6):1379-1388. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1496768. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30081709 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Co-administered Tag-Less Toxoid Fusion 3xSTaN12S-mnLTR192G/L211A and CFA/I/II/IV MEFA (Multiepitope Fusion Antigen) Induce Neutralizing Antibodies to 7 Adhesins (CFA/I, CS1-CS6) and Both Enterotoxins (LT, STa) of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC).Front Microbiol. 2018 Jun 5;9:1198. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01198. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29922268 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies derived from a toxoid MEFA (multiepitope fusion antigen) show neutralizing activities against heat-labile toxin (LT), heat-stable toxins (STa, STb), and Shiga toxin 2e (Stx2e) of porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC).Vet Microbiol. 2017 Apr;202:79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.02.002. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 26878972 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin and heat-labile toxin toxoid fusion 3xSTaN12S-dmLT induces neutralizing anti-STa antibodies in subcutaneously immunized mice.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2016 Nov 1;363(21):fnw246. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnw246. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27810884 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Newly Identified Functions Associated With the Heat-Labile Toxin of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Aug 13;9:292. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00292. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31456954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Heat-Labile Toxin (LT) Enzymatic Subunit Epitopes in LT Enterotoxicity and Immunogenicity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jul 17;84(15):e00849-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00849-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29802193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO (1999) The World. Health Rep: 1999: Making a Difference. Geneva: WHO.
-
- DuPont HL (2008) Systematic review: prevention of travellers' diarrhoea. Alimen. Pharmacol Ther 27: 741-751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

