F11R expression upon hypoxia is regulated by RNA editing
- PMID: 24147060
- PMCID: PMC3797694
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077702
F11R expression upon hypoxia is regulated by RNA editing
Abstract
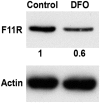
F11R is a cell adhesion molecule found on the surface of human platelets. It plays a role in platelet aggregation, cell migration and cell proliferation. F11R is subjected to RNA editing, a post-transcriptional modification which affects RNA structure, stability, localization, translation and splicing. RNA editing in the 3'UTR of F11R and RNA levels are increased upon hypoxia. We therefore set to examine if RNA editing plays a role in the increase of F11R RNA seen upon hypoxic conditions. We show that ADAR1, but not ADAR2, takes part in the editing of F11R however editing alone is not sufficient for obtaining an elevation in RNA levels. In addition we show that hyper-edited mature mRNAs are retained in the nucleus and are associated with p54(nrb). We therefore conclude that hypoxia-induced edited RNAs of F11R are preferentially stabilized and accumulate in the nucleus preventing their export to the cytoplasm for translation. This mechanism may be used by additional proteins in the cell as part of the cell's effort to reduce metabolism upon hypoxic stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
3'UTR RNA editing driven by ADAR1 modulates MDM2 expression in breast cancer cells.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 May 17;25(1):103. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01611-3. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40381037 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic structure, organization and promoter analysis of the human F11R/F11 receptor/junctional adhesion molecule-1/JAM-A.Gene. 2006 Jan 17;366(1):128-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.08.025. Epub 2005 Dec 5. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16337094
-
F11R RNA trinucleotide over-edited by ADAR in gastric and colorectal cancers: Cross-cohort validation, gene expression regulation, and diagnostic significance.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Sep 24;726:150213. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.150213. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38964186
-
What do editors do? Understanding the physiological functions of A-to-I RNA editing by adenosine deaminase acting on RNAs.Open Biol. 2020 Jul;10(7):200085. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200085. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32603639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAR RNA editing in human disease; more to it than meets the I.Hum Genet. 2017 Sep;136(9):1265-1278. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1837-0. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28913566 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary restriction induces posttranscriptional regulation of longevity genes.Life Sci Alliance. 2019 Jun 28;2(4):e201800281. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201800281. Print 2019 Aug. Life Sci Alliance. 2019. PMID: 31253655 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear paraspeckles function in mediating gene regulatory and apoptotic pathways.Noncoding RNA Res. 2019 Nov 21;4(4):128-134. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2019.11.002. eCollection 2019 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2019. PMID: 32072080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Many Faces of Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Sep 20;29(9):922-935. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7293. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28793797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in carcinogenesis.Mol Oncol. 2019 Jan;13(1):46-60. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12404. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30430751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NEAT1 and Paraspeckles in Cancer Development and Chemoresistance.Noncoding RNA. 2020 Oct 30;6(4):43. doi: 10.3390/ncrna6040043. Noncoding RNA. 2020. PMID: 33143162 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

