Dorsal and ventral hippocampus modulate autonomic responses but not behavioral consequences associated to acute restraint stress in rats
- PMID: 24147071
- PMCID: PMC3798415
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077750
Dorsal and ventral hippocampus modulate autonomic responses but not behavioral consequences associated to acute restraint stress in rats
Abstract
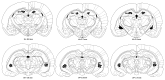
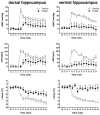
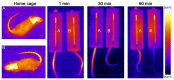
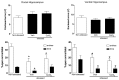
Recent evidence has suggested that the dorsal (DH) and the ventral (VH) poles of the hippocampus are structurally, molecularly and functionally different regions. While the DH is preferentially involved in the modulation of spatial learning and memory, the VH modulates defensive behaviors related to anxiety. Acute restraint is an unavoidable stress situation that evokes marked and sustained autonomic changes, which are characterized by elevated blood pressure (BP), intense heart rate (HR) increases, skeletal muscle vasodilatation and cutaneous vasoconstriction, which are accompanied by a rapid skin temperature drop followed by body temperature increases. In addition to those autonomic responses, animals submitted to restraint also present behavioral changes, such as reduced exploration of the open arms of an elevated plus-maze (EPM), an anxiogenic-like effect. In the present work, we report a comparison between the effects of pharmacological inhibition of DH and VH neurotransmission on autonomic and behavioral responses evoked by acute restraint stress in rats. Bilateral microinjection of the unspecific synaptic blocker cobalt chloride (CoCl2, 1mM) into the DH or VH attenuated BP and HR responses, as well as the decrease in the skin temperature, elicited by restraint stress exposure. Moreover, DH or VH inhibition before restraint did not change the delayed increased anxiety behavior observed 24 h later in the EPM. The present results demonstrate for the first time that both DH and VH mediate stress-induced autonomic responses to restraint but they are not involved in the modulation of the delayed emotional consequences elicited by such stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Behavioral and autonomic responses to acute restraint stress are segregated within the lateral septal area of rats.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023171. Epub 2011 Aug 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21858017 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of dorsal hippocampus glutamatergic and nitrergic neurotransmission in autonomic responses evoked by acute restraint stress in rats.Neuroscience. 2014 Jan 31;258:364-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.022. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24269610
-
Role of the endocannabinoid system in the dorsal hippocampus in the cardiovascular changes and delayed anxiety-like effect induced by acute restraint stress in rats.J Psychopharmacol. 2019 May;33(5):606-614. doi: 10.1177/0269881119827799. Epub 2019 Feb 21. J Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30789299
-
Role of endocannabinoid neurotransmission in the insular cortex on cardiovascular, autonomic and behavioral responses evoked by acute restraint stress in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2025 Jun 15;271:110404. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2025.110404. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Neuropharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40049238
-
Paraventricular nucleus modulates autonomic and neuroendocrine responses to acute restraint stress in rats.Auton Neurosci. 2010 Dec 8;158(1-2):51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2010.06.003. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Auton Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20594922
Cited by
-
Sex-specific hippocampus volume changes in obstructive sleep apnea.Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Jul 27;20:305-317. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.07.027. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30101062 Free PMC article.
-
Entanglement between thermoregulation and nociception in the rat: the case of morphine.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Dec 1;116(6):2473-2496. doi: 10.1152/jn.00482.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 7. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27605533 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Variable Stress and Cafeteria Diet Combination Exacerbate Microglia and c-fos Activation but Not Experimental Anxiety or Depression in a Menopause Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1455. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031455. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338735 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic, GABAergic, and endocannabinoid neurotransmissions within the dorsal hippocampus modulate the cardiac baroreflex function in rats.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Feb;470(2):395-411. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2083-y. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29143219
-
Storage of passive motion pattern in hippocampal CA1 region depends on CaMKII/CREB signaling pathway in a motion sickness rodent model.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 23;7:43385. doi: 10.1038/srep43385. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28230177 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

