Inter-laboratory assessment of a prototype multiplex kit for determination of recent HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 24147075
- PMCID: PMC3798393
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077765
Inter-laboratory assessment of a prototype multiplex kit for determination of recent HIV-1 infection
Abstract
Background: Accurate and reliable laboratory-based assays are needed for estimating HIV-1 incidence from cross-sectional samples. We recently described the development of a customized, HIV-1-specific Bio-Plex assay that allows for the measurement of HIV-specific antibody levels and avidity to multiple analytes for improved HIV-1 incidence estimates.
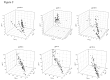
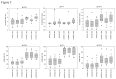
Methods: To assess intra- and inter-laboratory assay performance, prototype multiplex kits were developed and evaluated by three distinct laboratories. Longitudinal seroconversion specimens were tested in parallel by each laboratory and kit performance was compared to that of an in-house assay. Additionally, the ability of the kit to distinguish recent from long-term HIV-1 infection, as compared to the in-house assay, was determined by comparing the reactivity of known recent (infected <6 months) and long-term (infected >12 months) drug naïve specimens.
Results: Although the range of reactivity for each analyte varied between the prototype kit and in-house assay, a measurable distinction in reactivity between recent and long-term specimens was observed with both assays in all three laboratories. Additionally, kit performance was consistent between all three laboratories. The intra-assay coefficient of variation (CV), between sample replicates for all laboratories, ranged from 0.5% to 6.1%. The inter-laboratory CVs ranged from 8.5% to 21.3% for gp160-avidity index (a) and gp120-normalized mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) value (n), respectively.
Conclusion: We demonstrate the feasibility of producing a multiplex kit for measuring HIV antibody levels and avidity, with the potential for improved incidence estimates based on multi-analyte algorithms. The availability of a commercial kit will facilitate the transfer of technology among diverse laboratories for widespread assay use.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Performance characteristics of an antibody-based multiplex kit for determining recent HIV-1 infection.PLoS One. 2017 May 4;12(5):e0176593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176593. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28472089 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a multiplex assay for estimation of HIV-1 incidence.PLoS One. 2013 May 22;8(5):e64201. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064201. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23717568 Free PMC article.
-
Development and characterization of a bead-based, multiplex assay for estimation of recent HIV type 1 infection.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012 Feb;28(2):188-97. doi: 10.1089/aid.2011.0037. Epub 2011 Jun 17. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012. PMID: 21585287
-
Determination of the mean duration of recent infection and false recency rate for the HIV triplex multiplex bead assay.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 25;19(10):e0311829. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311829. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39453903 Free PMC article.
-
Application of laboratory methods for estimation of HIV-1 incidence.Indian J Med Res. 2005 Apr;121(4):510-8. Indian J Med Res. 2005. PMID: 15817960 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreasing Proportion of Recent Infections among Newly Diagnosed HIV-1 Cases in Switzerland, 2008 to 2013 Based on Line-Immunoassay-Based Algorithms.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 31;10(7):e0131828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131828. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26230082 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of dried blood spots with a multiplex assay for measuring recent HIV-1 infection.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 18;9(9):e107153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107153. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25232736 Free PMC article.
-
Performance characteristics of an antibody-based multiplex kit for determining recent HIV-1 infection.PLoS One. 2017 May 4;12(5):e0176593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176593. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28472089 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Evaluation of a Modified Fourth-Generation Human Immunodeficiency Virus Enzyme Immunoassay for Cross-Sectional Incidence Estimation in Clade B Populations.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2016 Aug;32(8):756-62. doi: 10.1089/AID.2015.0198. Epub 2016 May 5. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2016. PMID: 26988426 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

