Elimination of schistosomiasis transmission in Zanzibar: baseline findings before the onset of a randomized intervention trial
- PMID: 24147165
- PMCID: PMC3798599
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002474
Elimination of schistosomiasis transmission in Zanzibar: baseline findings before the onset of a randomized intervention trial
Erratum in
- PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013 Oct;7(10). doi: 10.1371/annotation/d5135174-e4ff-44c6-9c04-17c072a4fd0b doi: 10.1371/annotation/d5135174-e4ff-44c6-9c04-17c072a4fd0b
Abstract
Background: Gaining and sustaining control of schistosomiasis and, whenever feasible, achieving local elimination are the year 2020 targets set by the World Health Organization. In Zanzibar, various institutions and stakeholders have joined forces to eliminate urogenital schistosomiasis within 5 years. We report baseline findings before the onset of a randomized intervention trial designed to assess the differential impact of community-based praziquantel administration, snail control, and behavior change interventions.
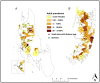
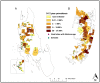
Methodology: In early 2012, a baseline parasitological survey was conducted in ~20,000 people from 90 communities in Unguja and Pemba. Risk factors for schistosomiasis were assessed by administering a questionnaire to adults. In selected communities, local knowledge about schistosomiasis transmission and prevention was determined in focus group discussions and in-depths interviews. Intermediate host snails were collected and examined for shedding of cercariae.
Principal findings: The baseline Schistosoma haematobium prevalence in school children and adults was 4.3% (range: 0-19.7%) and 2.7% (range: 0-26.5%) in Unguja, and 8.9% (range: 0-31.8%) and 5.5% (range: 0-23.4%) in Pemba, respectively. Heavy infections were detected in 15.1% and 35.6% of the positive school children in Unguja and Pemba, respectively. Males were at higher risk than females (odds ratio (OR): 1.45; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.03-2.03). Decreasing adult age (OR: 1.04; CI: 1.02-1.06), being born in Pemba (OR: 1.48; CI: 1.02-2.13) or Tanzania (OR: 2.36; CI: 1.16-4.78), and use of freshwater (OR: 2.15; CI: 1.53-3.03) showed higher odds of infection. Community knowledge about schistosomiasis was low. Only few infected Bulinus snails were found.
Conclusions/significance: The relatively low S. haematobium prevalence in Zanzibar is a promising starting point for elimination. However, there is a need to improve community knowledge about disease transmission and prevention. Control measures tailored to the local context, placing particular attention to hot-spot areas, high-risk groups, and individuals, will be necessary if elimination is to be achieved.
Conflict of interest statement
The molluscicide niclosamide was donated by Bayer for the control of intermediate host snails in Zanzibar. This does not alter our adherence to all PLOS NTDs policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, et al. (2012) Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 380: 2197–2223. - PubMed
-
- Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J (2006) Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis 6: 411–425. - PubMed
-
- Utzinger J, Becker SL, Knopp S, Blum J, Neumayr AL, et al. (2012) Neglected tropical diseases: diagnosis, clinical management, treatment and control. Swiss Med Wkly 142: w13727. - PubMed
-
- WHO (2012) Accelerating work to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases – a roadmap for implementation. Geneva: World Health Organization. 42 p.
-
- WHO (2012) The London Declaration. Uniting to combat neglected tropical diseases. Ending the Neglect & Reaching 2020 Goals. Table of commitments. Available: http://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/NTD_London_Event_Table_Commitments.... Accessed 17 July 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

