Neural circuit modulation during deep brain stimulation at the subthalamic nucleus for Parkinson's disease: what have we learned from neuroimaging studies?
- PMID: 24147633
- PMCID: PMC5349222
- DOI: 10.1089/brain.2013.0193
Neural circuit modulation during deep brain stimulation at the subthalamic nucleus for Parkinson's disease: what have we learned from neuroimaging studies?
Abstract
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) targeting the subthalamic nucleus (STN) represents a powerful clinical tool for the alleviation of many motor symptoms that are associated with Parkinson's disease. Despite its extensive use, the underlying therapeutic mechanisms of STN-DBS remain poorly understood. In the present review, we integrate and discuss recent literature examining the network effects of STN-DBS for Parkinson's disease, placing emphasis on neuroimaging findings, including functional magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography, and single-photon emission computed tomography. These techniques enable the noninvasive detection of brain regions that are modulated by DBS on a whole-brain scale, representing a key experimental strength given the diffuse and far-reaching effects of electrical field stimulation. By examining these data in the context of multiple hypotheses of DBS action, generally developed through clinical and physiological observations, we define a multitude of consistencies and inconsistencies in the developing literature of this rapidly moving field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
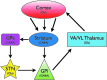
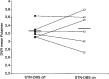

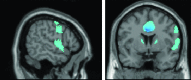
References
-
- Alexander GE, DeLong MR, Strick PL. 1986. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci 9:357–381 - PubMed
-
- Arai N, Yokochi F, Ohnishi T, Momose T, Okiyama R, Taniguchi M, et al. . 2008. Mechanisms of unilateral STN-DBS in patients with Parkinson's disease: a PET study. J Neurol 255:1236–1243 - PubMed
-
- Arle JE, Apetauerova D, Zani J, Deletis DV, Penney DL, Hoit D, et al. . 2008. Motor cortex stimulation in patients with Parkinson disease: 12-month follow-up in 4 patients. J Neurosurg 109:133–139 - PubMed
-
- Bandettini PA, Wong EC, Hinks RS, Tikofsky RS, Hyde JS. 1992. Time course EPI of human brain function during task activation. Magn Reson Med 25:390–397 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

