A multi-colour/multi-affinity marker set to visualize phosphoinositide dynamics in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 24147788
- PMCID: PMC3981938
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.12358
A multi-colour/multi-affinity marker set to visualize phosphoinositide dynamics in Arabidopsis
Abstract
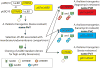
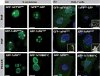
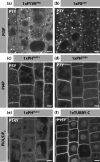
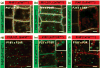
Phosphatidylinositolphosphates (PIPs) are phospholipids that contain a phosphorylated inositol head group. PIPs represent a minor fraction of total phospholipids, but are involved in many regulatory processes, such as cell signalling and intracellular trafficking. Membrane compartments are enriched or depleted in specific PIPs, providing a unique composition for these compartments and contributing to their identity. The precise subcellular localization and dynamics of most PIP species is not fully understood in plants. Here, we designed genetically encoded biosensors with distinct relative affinities and expressed them stably in Arabidopsis thaliana. Analysis of this multi-affinity 'PIPline' marker set revealed previously unrecognized localization of various PIPs in root epidermis. Notably, we found that PI(4,5)P2 is able to localize PIP2 -interacting protein domains to the plasma membrane in non-stressed root epidermal cells. Our analysis further revealed that there is a gradient of PI4P, with the highest concentration at the plasma membrane, intermediate concentration in post-Golgi/endosomal compartments, and the lowest concentration in the Golgi. Finally, we also found a similar gradient of PI3P from high in late endosomes to low in the tonoplast. Our library extends the range of available PIP biosensors, and will allow rapid progress in our understanding of PIP dynamics in plants.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; endosome; lipid binding domain; lipid signalling; membrane trafficking; phosphoinositide; sensor; technical advance.
© 2013 The Authors The Plant Journal © 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Detection of Plasma Membrane Phosphoinositide Dynamics Using Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Protein Probes.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2251:73-89. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1142-5_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33481232
-
Subcellular Localization of PI3P in Arabidopsis.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2177:109-118. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0767-1_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32632809
-
A map of the subcellular distribution of phosphoinositides in the erythrocytic cycle of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum.Int J Parasitol. 2018 Jan;48(1):13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Int J Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29154995
-
Physiological Functions of Phosphoinositide-Modifying Enzymes and Their Interacting Proteins in Arabidopsis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1111:139-157. doi: 10.1007/5584_2018_295. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30499079 Review.
-
Diversity of phosphoinositide binding proteins in Entamoeba histolytica.Parasitol Int. 2021 Aug;83:102367. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2021.102367. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Parasitol Int. 2021. PMID: 33905816 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular requirements for PIN polar cargo clustering in Arabidopsis thaliana.New Phytol. 2021 Jan;229(1):351-369. doi: 10.1111/nph.16887. Epub 2020 Sep 18. New Phytol. 2021. PMID: 32810889 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipids in Salt Stress Response.Plants (Basel). 2021 Oct 17;10(10):2204. doi: 10.3390/plants10102204. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34686013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic analysis of the Arabidopsis TIR1/AFB auxin receptors reveals both overlapping and specialized functions.Elife. 2020 Feb 18;9:e54740. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54740. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32067636 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring lipid-protein interactions in plant membranes.J Exp Bot. 2024 Sep 11;75(17):5251-5266. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae199. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38708855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipids mediate polar sorting of PIN2 through phosphoinositide consumption at the trans-Golgi network.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 13;12(1):4267. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24548-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34257291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ago T, Takeya R, Hiroaki H, Kuribayashi F, Ito T, Kohda D, Sumimoto H. The PX Domain as a Novel Phosphoinositide- Binding Module. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;287:733–738. - PubMed
-
- Balla A, Tuymetova G, Tsiomenko A, Várnai P, Balla T. A Plasma Membrane Pool of Phosphatidylinositol 4- Phosphate Is Generated by Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase Type-III Alpha: Studies with the PH Domains of the Oxysterol Binding Protein and FAPP1. Molecular biology of the cell. 2005;16:1282–1295. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bravo J, Karathanassis D, Pacold CM, Pacold ME, Ellson CD, Anderson KE, Butler PJ, Lavenir I, Perisic O, Hawkins PT, Stephens L, Williams RL. The crystal structure of the PX domain from p40(phox) bound to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. Mol Cell. 2001;8:829–839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

